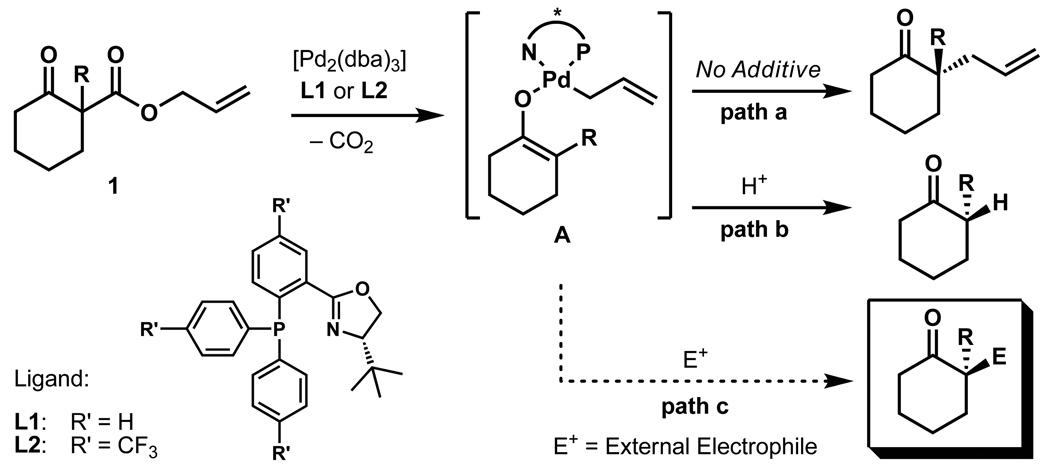
Figure 1. Concept for the enantioselective functionalisation of palladium-enolates.
Three pathways for the palladium catalyzed generation α-functionalised ketones are shown. A palladium catalyst generated from [Pd2(dba)3] and ligand L undergoes oxidative addition to β-ketoester 1 following the loss of CO2 to form an enolate intermediate A. This palladium enolate can either react following path a to yield enantioenriched α-alkylated products or following path b in the presence of a proton source to give α-protonated products. The envisioned path c would form miscellaneous enantioenriched α-substituted ketones depending on other electrophilic additives "E+" that intercept enolate A.