Figure 6.
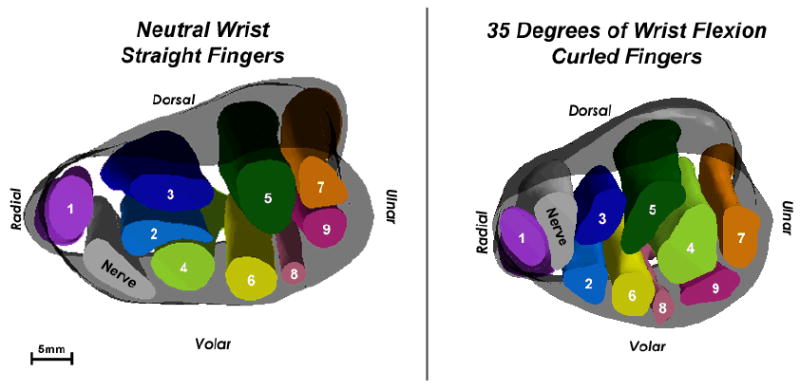
3D isosurface models of Subject 2’s wrist in neutral (left) and in 35 degrees of flexion (right). This again is a proximal-to-distal view. The flattening ratio of the nerve decreased very slightly between neutral and flexion, indicating minimal changes to the shape of the nerve. However, in the 3D models, a dramatic change in position is evident for the nerve, the superficial long tendon (2), and the tendons of the 4th and 5th digits (6-9).
