Fig. 4.
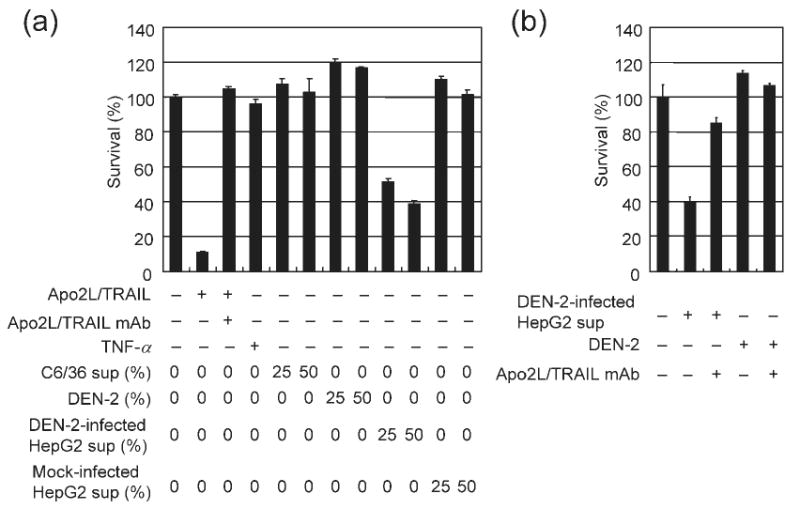
Apo2L/TRAIL is released from DEN-2-infected HepG2 cells. (a) HepG2 cells were either mock-treated or infected with DEN-2 (m.o.i. of 8) and then cultured for 72 h. Supernatant from infected or mock-treated HepG2 cells or C6/36 cell supernatant was added to Apo2L/TRAIL-sensitive Jurkat cells as a 25 or 50% mixture with basal medium. Alternatively, Apo2L/TRAIL (100 ng ml−1), TNF-α (100 ng ml−1) or DEN-2 (1 or 2 × 106 f.f.u. ml−1) was added as indicated. Cell viability was assayed 24 h after supernatant transfer and results are shown as percentage survival of Jurkat cells following treatment compared with treatment with basal medium only. Anti-Apo2L/TRAIL mAb (10 μg ml−1) was used as an Apo2L/TRAIL specificity control. Values represent the mean±SD of triplicate measurements. (b) Supernatant from infected HepG2 cells (as a 50% mixture) and DEN-2 (2 × 106 f.f.u. ml−1) were added with basal medium to Jurkat cells as indicated. Anti-Apo2L/TRAIL mAb (10 μg ml−1) or control IgG1 (10 μg ml−1) was also added. Cell viability was assayed in Jurkat cells 24 h following supernatant transfer. Results are shown as percentage survival of Jurkat cells following treatment compared with treatment with basal medium only.
