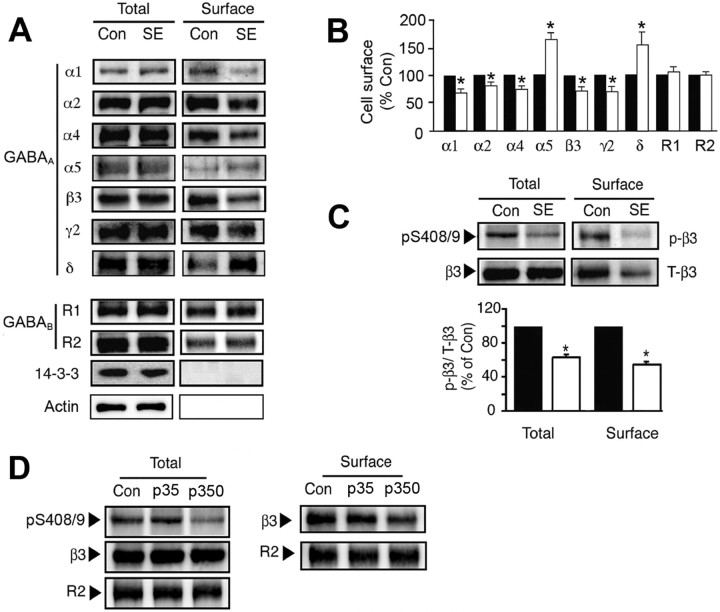
Figure 1.
The effects of SE on the cell surface stability and phosphorylation of GABAARs. A, B, SE modulates GABAA receptor surface expression levels. Hippocampal slices from control (Con) or SE were labeled with NHS-biotin and lysed, and biotinylated proteins were purified on avidin. A, Cell surface and total fractions (1/10 of input; In) were immunoblotted with antibodies against GABAA receptor α1–2, α4–5, β3, γ2, and δ subunits, GABAB R1 and R2 subunits, 14-3-3ζ, and actin. B, Data in SE (open bars) were normalized to the cell surface levels evident in control slices (filled bars; 100%). C, SE decreases the phosphorylation of S408/9 in the GABAAR β3 subunit. Top, Hippocampal slices from control and SE were subjected to biotinylation, and cell surface fractions were blotted with a phospho-specific antibody against S408/9 in the β3 subunit (p-β3) and anti-β3 antibodies (T-β3). Bottom, The ratio p-β3/T-β3 signals were then measured in control (filled bars) and SE (open bars) with values normalized to those in control (100%). In all panels, asterisks indicate significant difference from control (p < 0.01; Student's t test; n = 6–8). D, Hippocampal slices were prepared from Con, and animals were injected with 35 (p35) and 350 mg/kg (p350) pilocarpine, respectively. Slices were biotinylated, and cell surface and total fractions were isolated and immunoblotted with the respective antibodies as indicated.