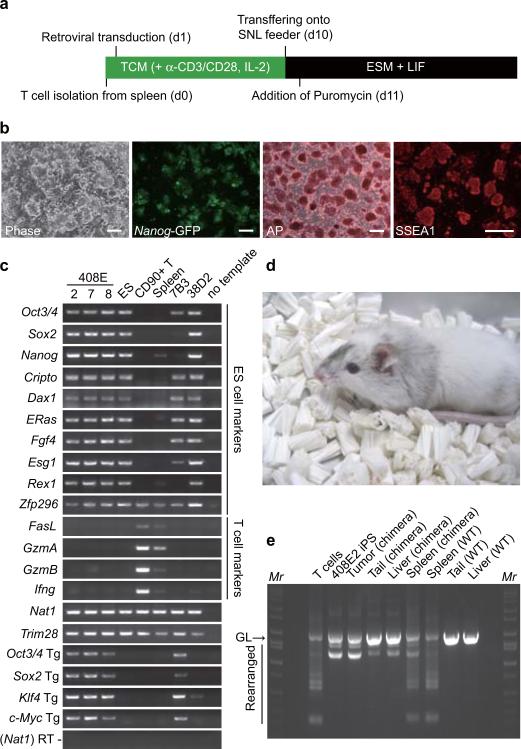
Figure 2. T-lymphocyte-derived iPS cells.
a. Protocol for iPS cell generation from mouse T-lymphocytes. TCM; T cell medium, ESM; ES cell medium.
b. A phase contrast image, Nanog-GFP expression, alkaline phosphatase staining, and SSEA1 staining of T cell-derived iPS cells (clone 408E2). Bars indicate 100 μm.
c. Expression of marker genes was examined by RT-PCR in T cell-derived iPS cells (clones 408E -2, -7 and -8), RF8 ES cells, T cells, Spleen, Fbx15-selected iPS cells from p53 wild-type MEF (clone 7B3), and Nanog-selected iPS cells from p53 wild-type MEF (clone 38D2)
d. A chimera mouse derived from clone 408E2. iPS cells were microinjected into blastocysts from ICR mice.
e. The V-(D)-J DNA rearrangement of the Tcrβ gene was confirmed by genomic PCR in iPS cells and a chimeric mouse. GL indicates the germline band.