Figure 1.
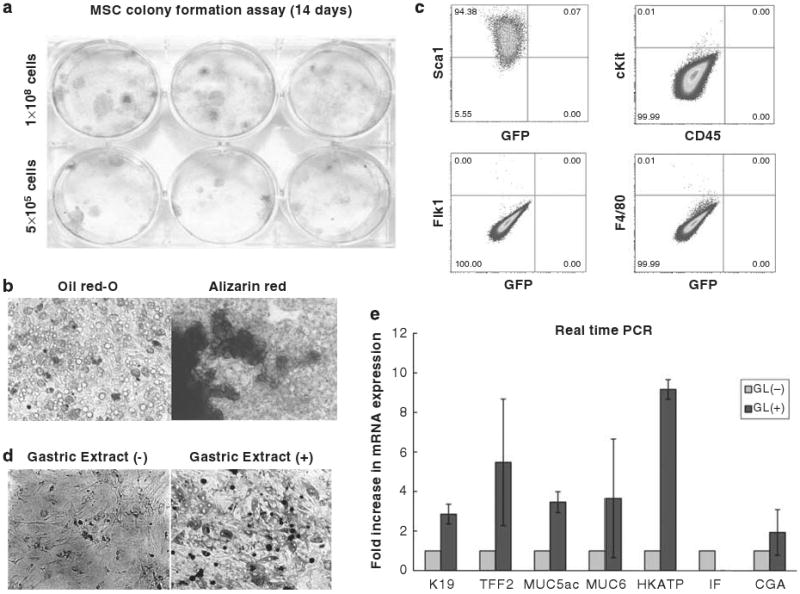
Establishment of bone marrow-derived MSC culture and induced expression of gastric phenotype markers after treatment with gastric tissue extract. (a) Colony formation of MSCs. 500 000 or 1 000 000 cells of MSC at passage 5–10 were seeded onto 6-well tissue culture plate and colonies were visualized with crystal violet staining 14 days after plating. (b) Adipocyte and osteocyte differentiation of MSCs. All established MSC cultures were incubated with adipocyte or osteocyte differentiation medium for 14 days and cells were stained with Oil red-O and Alizarin Red, respectively. (c) Expression of cell surface markers (Sca1, c-kit, CD45, Flk1, and F4/80) was analyzed by flow cytometry. Quadrant markers were set according to the profile of corresponding control IgG staining. Representative examples of three experiments. (d) Morphology of MSCs 5 days after treatment with gastric tissue extract. (e) Expression of gastric epithelial phenotype markers in MSCs after treatment with gastric tissue extract. MSCs were incubated with gastric tissue extract (GL) for 5 days and the mRNA expression of K19, TFF2, Muc5as, Muc6, H/K-ATPase, intrinsic factor (IF), and chromogranin A (CGA) were detected by real-time PCR. Fold increase in mRNA expression (light grey bar) was shown as compared with control cells, which were incubated with culture medium without gastric tissue extract (dark grey bar) was calculated (n = 3).
