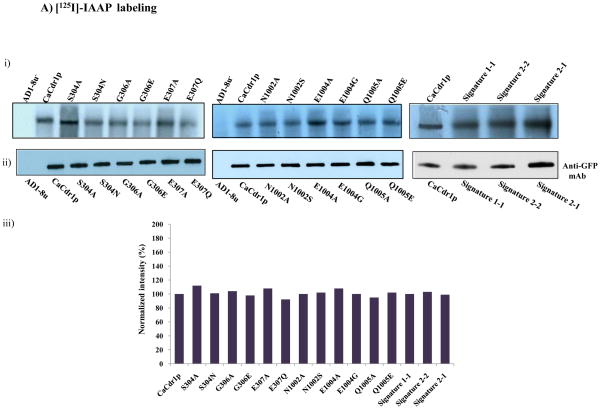
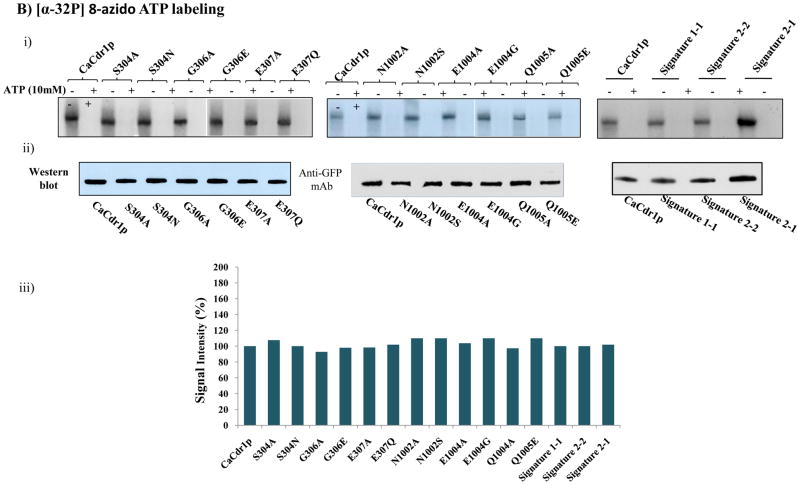
Fig. 5.
A). (i) Photoaffinity labeling of WT-CaCdr1p and its mutant variants with [125I]-IAAP. The PM fraction (30 μg protein) of cells expressing WT-CaCdr1p and its mutant variants were incubated with 7.5 nM [125I]-IAAP (2300 Ci/mmol). The samples were UV crosslinked and processed as described elsewhere [34]. (ii) Western blot analysis using anti-GFP antibody to ensure equal loading of WT-CaCdr1p and its Signature mutant variants (iii) Normalized incorporated [125I] IAAP labeling with Western blot intensity. The values are shown in percentage. B). Photoaffinity labeling of WT-CaCdr1p and its mutant variants with [α-32P] 8-azido ATP. The PM fraction (30 μg) of cells expressing the WT-CaCdr1p and its mutant variants were incubated with 10 μM [α-32P] 8-azido ATP 7.5 μCi/nmol at 4°C and competed with 10 mM cold ATP (+ATP lane) as described in [34]. (ii) Western blot analysis using anti-GFP antibody to ensure equal loading of WT-CaCdr1p and its Signature mutant variants (iii) Normalized incorporated [α-32P] 8-azido ATP labeling with Western blot intensity. The values are shown in percentage.