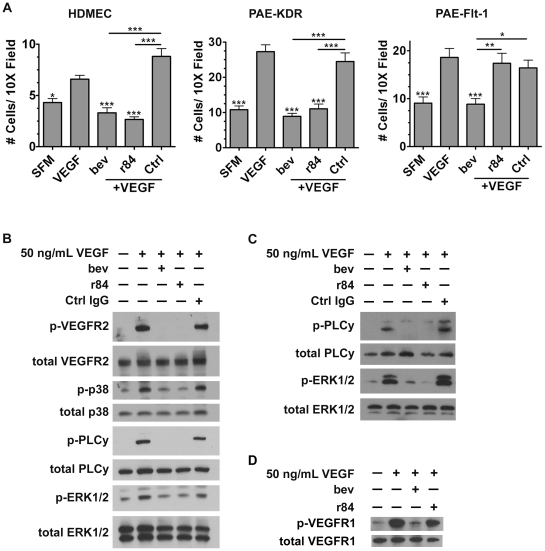
Figure 2. r84 reduces endothelial cell migration and signaling in vitro.
A, A modified Boyden chamber migration assay was used to assess the effect of r84, bevacizumab (bev) on VEGF-induced endothelial cell (EC) migration. 20,000 HDMEC, PAE-KDR, PAE-Flt-1 cells were plated on 8.0 µm cell culture inserts and allowed to migrate overnight towards SFM or human VEGF (100 ng/mL) +/− 500-fold molar excess antibody (bev, r84, control IgG). r84, bev block the VEGF-induced migration of VEGFR2-expressing ECs (A, HDMEC, PAE-KDR). Bev blocks VEGF-induced migration of endothelial cells expressing VEGR1, but r84 does not (A, PAE-Flt-1). Western blots of VEGF-induced signaling in PAE-KDR (B), HDMEC (C), and PAE-Flt-1 (D) lysates following stimulation of cells with 50 ng/mL human VEGF +/− 500-fold molar excess antibody (bev, r84, control IgG). r84 and bev block p-VEGFR2 and downstream phosphorylation (p38, PLCγ, ERK1/2) (B, C), but only bev blocks VEGF-induced VEGFR1 phosphorylation in PAE-Flt-1 stimulated cells (D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, statistical differences in A compared to VEGF alone, unless otherwise indicated.