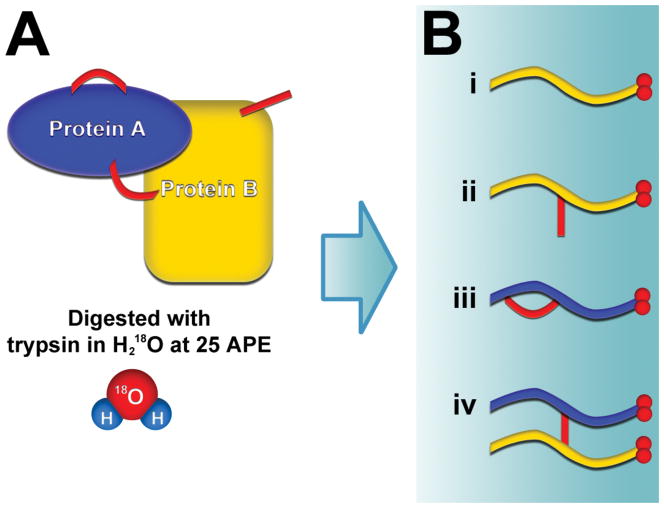
Figure 2.
Labeling procedure for the detection of crosslinked peptides. (A) Crosslinked proteins are digested with trypsin in buffer containing H218O at 25 atom percent excess. All resulting peptides become 18O labeled on their C-terminus. (B) Four possible types of peptides are produced: (i) unlinked peptides without crosslinker; (ii) dead-end peptides that contain hydrolyzed or aminolyzed crosslinker; (iii) loop-linked peptides where two lysines on a single peptide are linked to each other; (iv) interlinked peptides. Interlinked peptides are distinguished from the other peptides because they have twice the amount of labeling on their C-termini.