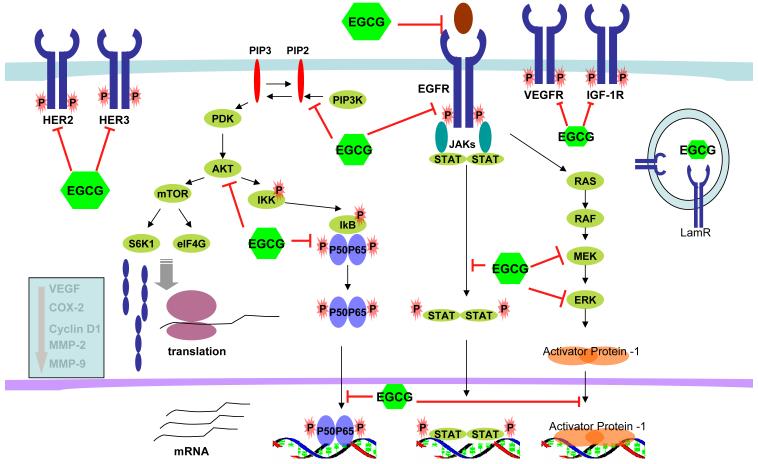
Figure 3. Molecular targets of EGCG.
Several signaling pathways are affected by EGCG at multiple levels. EGCG inhibits the ligand binding of EGFR and inhibits phosphorylation/activation of the receptor tyrosine kinases. It also inhibits several intracellular signaling pathways, including PI3K/Akt/mTOR, JAK/STAT, RAF/MEK/ERK/AP-1, and Akt/NF-κB. At the nuclear level, EGCG also inhibits the DNA binding of effector transcription factors, such as NF-κB, AP-1 and STAT. As a consequence, expression of molecules that are involved in cell proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion and inflammation are reduced.