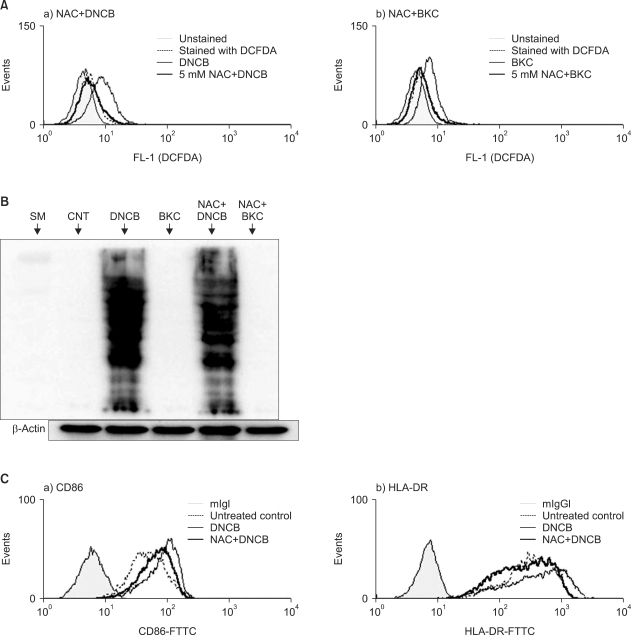
Fig. 4.
(A) Hapten and irritant-induced ROS diminished by N-acetyl L-cystein. MoDCs were pre-treated with 5 mM NAC for 30 min and then treated with 30µM DNCB or 20µM BKC. After 1 h they were stained with 3 mM CM-H2DCFDA and analyzed by flow cytometry. The histogram of chemical-treated MoDCs in the presence or the absence of NAC is expressed as a thick solid line or solid line, whereas a filled line or a dotted line indicates histograms of untreated DCs or of DCs stained with CM-H2DCFDA, respectively. Pre-treatment of MoDCs with 5 mM of NAC reduced the ROS production induced by DNCB significantly (the relative ROS increase with DNCB treatment was 3.8-fold while that with pre-treatment with NAC plus DNCB treatment was 0.56-fold. p≤0.0001). BKC-induced ROS production was decreased by pre-treatment with NAC (the relative ROS increase with BKC treatment was 2.6-fold while that with pre-treatment with NAC plus BKC treatment was 0.70-fold). Each experiment was repeated three times and one representative result is shown. (B) These carbonylated proteins were decreased slightly by NAC. Immature day 6 MoDCs were incubated with 20µM DNCB or 10µM BKC in the presence or absence of 5 mM NAC for 30 min. After 6 h, equal amounts of whole cell protein extracts were loaded in SDS gel and carbonylated proteins were detected using DNP antibody by Western blotting. Allergen DNCB but not irritant BKC induced protein carbonylation and the resulting carbonylated protein was decreased slightly by NAC. (C) NAC suppressed the augmentation of CD86 and HLA-DR molecules on MoDCs that were induced by contact allergen DNCB. MoDCs were cultured with DNCB in the presence or absence of pre-treatment 5 mM NAC. After 24 h their surface molecules were analyzed by flow cytometry. Thick solid line indicates the histogram of chemical-treated MoDCs with NAC; narrow solid line indicates treatment without NAC; filled line indicates non-treatment; dotted line indicates treatment with CD86 antibody only. Augmentation of CD86 and HLA-DR by DNCB was decreased by adding 10 mM NAC.