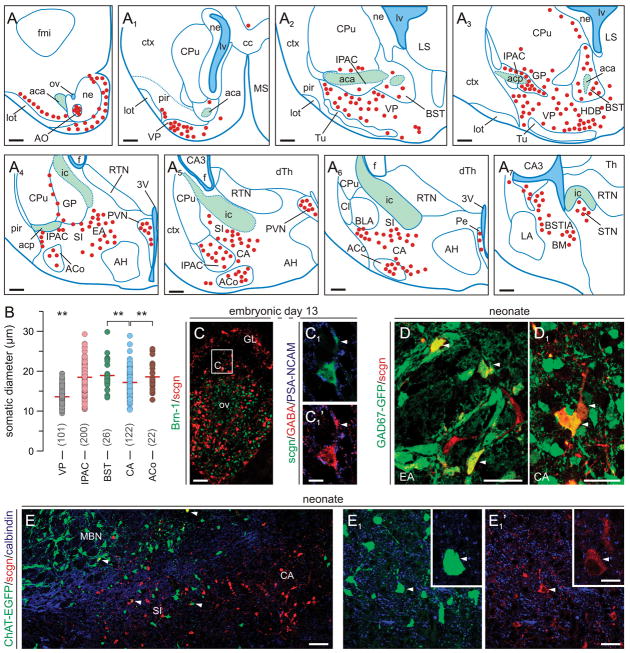
Fig. 5. Scgn in the neonatal mouse forebrain.
(A–A7) Schematic presentation of the regional distribution of scgn+ neurons in coronal sections along the anterior-posterior axis of the new-born mouse brain with a sampling interval of 560 μm. Red circles correspond to scgn+ cells, blue lines demarcate particular nuclei, and green areas identify major axonal pathways. (B) Somatic diameters of scgn+ neurons in the VP and subdivisions of the amygdaloid complex (IPAC, BST, CA, ACo). **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). (C-C1) Scgn+ neurons in the olfactory bulb contain GABA by E13. Arrowheads point to the leading edge. (D,D1) Scgn immunoreactivity decorates GABAergic neurons in the extended (EA) and central amygdala (CA). (E-E1′) A subset of GFP-tagged cholinergic neurons inhabiting the prospective substantia innominata (SI) are scgn+ (arrowheads). Abbreviations are listed in Supporting Table 1. Scale bars = 500 μm (A-A7), 200 μm (C), 20 μm (C1,C2).