FIGURE 4.
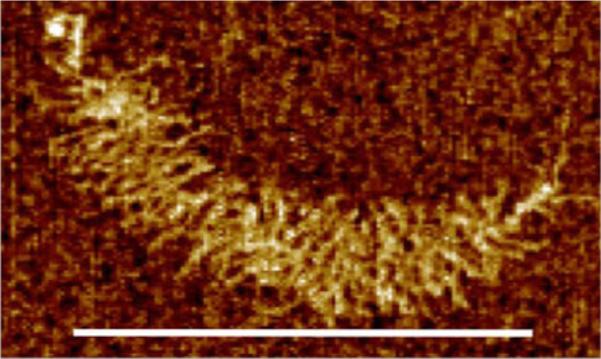
AFM image of a single aggrecan monomer extracted from human articular cartilage, consisting of a core protein substituted with almost 100 chondroitin sulfate and 10–20 keratan sulfate glycosaminoglycan chains. Scale bar = 300 nm. The globular G1 domain at the left-most (N-terminal) end can bind to hyaluronic acid (HA), stabilized by co-binding of a 45 kDa link protein, thereby forming supramolecular aggregates containing as many as 100 aggrecan monomers. Enzymatic cleavage of aggrecan by aggrecanase enzymes (e.g., ADAMTS-4, -5) at 5 or more sites along the core protein causes degradation and loss of these monomers in diseases such as osteoarthritis (Image courtesy of H.-Y. Lee, A.J. Grodzinsky, and C. Ortiz).
