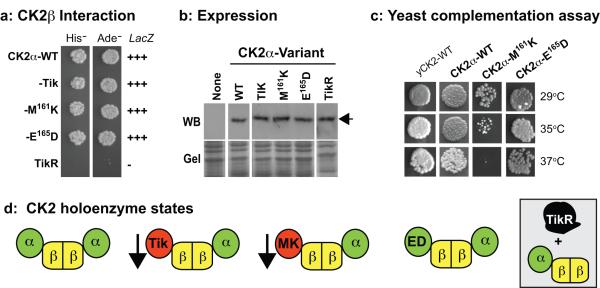
Figure-2. Biochemical analysis of CK2α variants in yeast.
(a) Interaction trap analysis. Cells expressing CK2α-variants plus CK2β were tested for induction of the reporters on media lacking His or Ade, and for LacZ, which is reported as strong (+++) or none (−). (b) Expression of CK2α variants. Arrow denotes dCK2α protein. (c) Complementation of the lethality of yeast lacking endogenous CK2. Yeast cells were rescued by a plasmid encoding yeast-CK2 (yCK2-WT), or were rescued by plasmids containing the indicated Drosophila CK2α-variants. Growth was assessed at the indicated temperatures. (d) Tik and CK2α-M161K are deficient for kinase activity (arrow), but interact normally with CK2β. Both CK2α-E165D and CK2α-WT retain activity and CK2β-binding. TikR is non-functional for structure and activity.