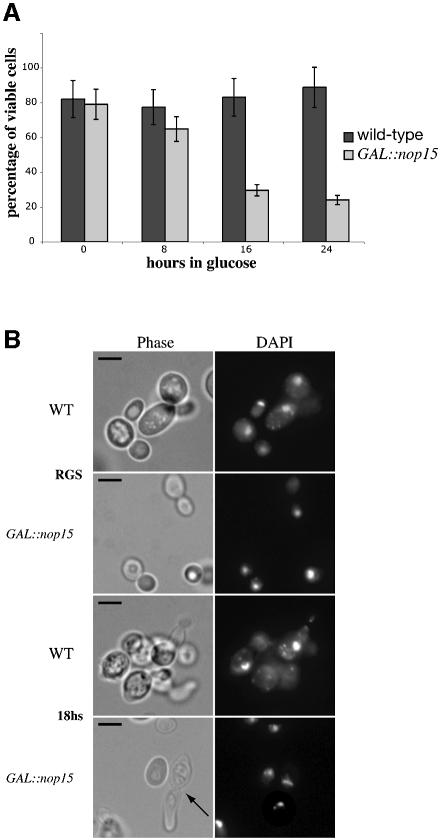
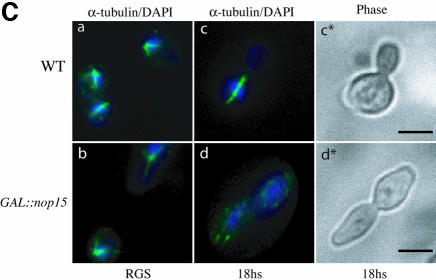
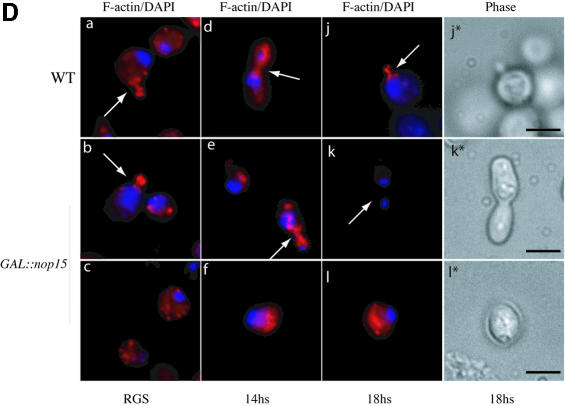
Fig. 5. Depletion of Nop15p leads to a cell cycle defect. (A) Percentage of cells from wild-type and GAL::nop15 strains that remain viable when plated on fresh, pre-warmed YRGS plates following incubation in glucose medium for the times indicated. Viability was determined by comparing the total number of cells plated with the number of colonies formed at each time point. (B) Cell morphology. (C) Staining with anti-tubulin. (D) Staining with rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin to detect F-actin. Wild-type and GAL::nop15 strains were examined during growth in RGS medium and following transfer to glucose medium for 14 or 18 h. The position of the nucleus was visualized by DAPI staining. In (C) and (D), the figures indicated with an asterisk show phase contrast images of cells in the corresponding immunofluorescence images. The bar represents 10 µm and arrows indicate the position of the bud neck.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.