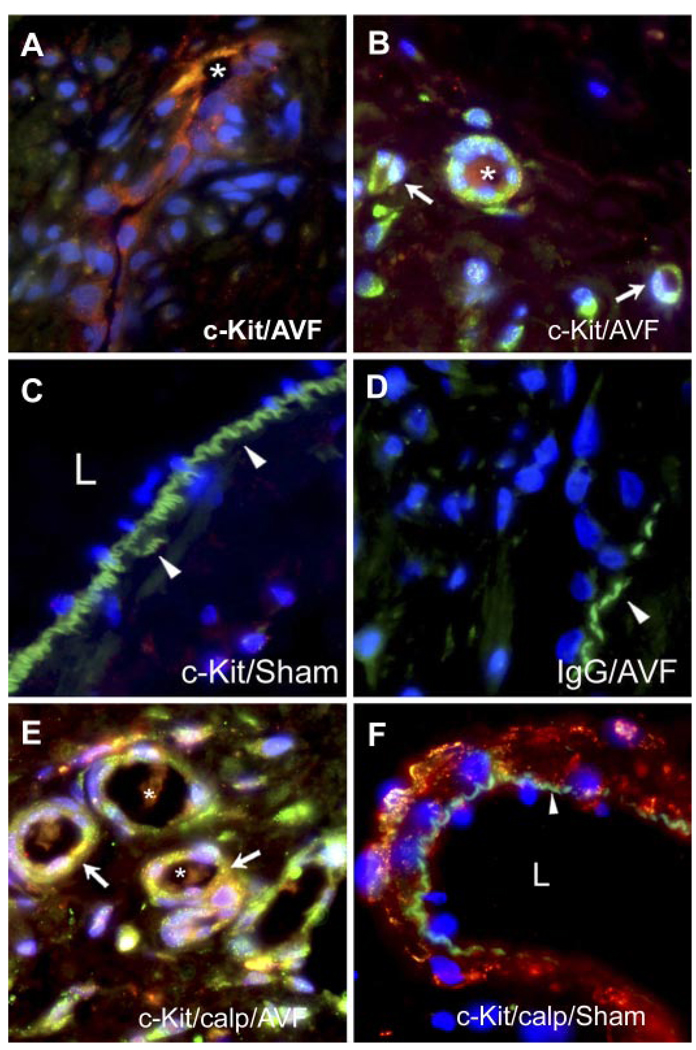
Fig. 2.
Immunohistochemistry for c-Kit in the venous limb of the AV fistula and sham-operated rats. A: c-Kit-positive cells within a longitudinal section of a microvessel within the intimal plaque of the AV fistula; the lumen of the microvessel is marked by an asterisk. B: c-Kit-positive cells within the adventitia of the venous limb of the AV fistula. c-Kit-positive cells forming signet ring structures are marked by white arrows. Also displayed is a microvessel formed from multiple c-Kit-positive cells that exhibits a patent lumen marked by an asterisk. C: absence of c-Kit-positive immunoreactivity in the venous limb in sham-operated rats. Arrowheads indicate the internal elastic lamina, and L indicates the lumen of the vein. D: absence of staining with IgG isotype-matched control in the venous limb of the AV fistula. E: neovascularized zone in the adventitia of the venous limb of the AV fistula showing dual staining for c-Kit (green) and calponin (calp; red) to reveal a merged image (yellow) and that is marked by white arrows; patent lumina are marked by asterisks. F: combined staining for c-Kit and calponin showing only calponin immunoreactivity in the venous limb in the sham-operated rat and an absence of c-Kit immunoreactivity. The arrowhead indicates the internal elastic lamina, and L indicates the lumen.