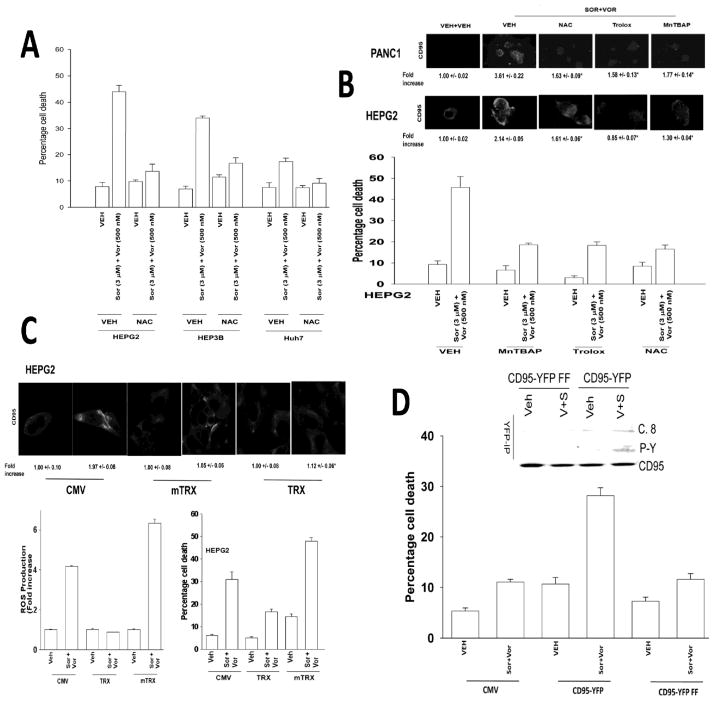
Figure 2. ROS play a central role in CD95 activation and apoptosis.
Panel A. Hepatoma cells were pre-treated with N-acetyl cysteine and then with sorafenib and vorinostat. Viability was determined by trypan blue after 48h (n = 3, +/− SEM). Panel B. Lower Panel: HEPG2 cells were pre-treated with N-acetyl cysteine, Trolox or MnTBAP and with sorafenib and vorinostat. ROS levels were measured 15 min after exposure (n = 2, +/− SEM). Upper IHC: PANC1 and HEPG2 cells were pre-treated with N-acetyl cysteine, Trolox or MnTBAP and 30 min later treated with sorafenib and vorinostat. Cells were fixed after 6h and cell surface CD95 levels determined. Panel C. Lower graphs: Left: HEPG2 cells were transfected with empty vector (CMV) or to express either wild type Thioredoxin (TRX) or mutant inactive Thioredoxin (mTRX). Twenty-four h after transfection cells were treated with sorafenib (3.0 μM) and vorinostat (500 nM). ROS levels were measured 15 min after treatment (n = 2, +/− SEM); Right: HEPG2 cells were transfected to express either TRX or mTRX. Twenty-four h after transfection cells were treated with, sorafenib, vorinostat or both drugs. Cells were isolated after 48h and viability determined by trypan blue (n = 3, +/− SEM). Upper IHC: HEPG2 cells were transfected to express TRX or mTRX. Twenty-four h after transfection cells were treated with sorafenib and vorinostat. Six h after treatment cells were fixed and CD95 plasma membrane levels determined (n = 2, +/− SEM). Panel D. Lower Graph: HuH7 cells were transfected to express CD95-YFP or CD95-YFP FF. Twenty-four h after transfection cells were treated with sorafenib (3.0 μM) and vorinostat (500 nM). Cells were isolated after 48h and viability determined by trypan blue (n = 2, +/− SEM). Upper section: HuH7 cells were transfected to express CD95-YFP or CD95-YFP FF. Twenty-four h after transfection cells were treated with sorafenib and vorinostat. Cells were isolated after 6h and CD95 immunoprecipitated to determine DISC formation and CD95 tyrosine phosphorylation.