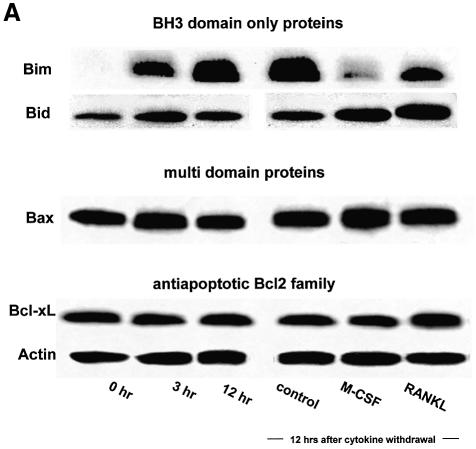
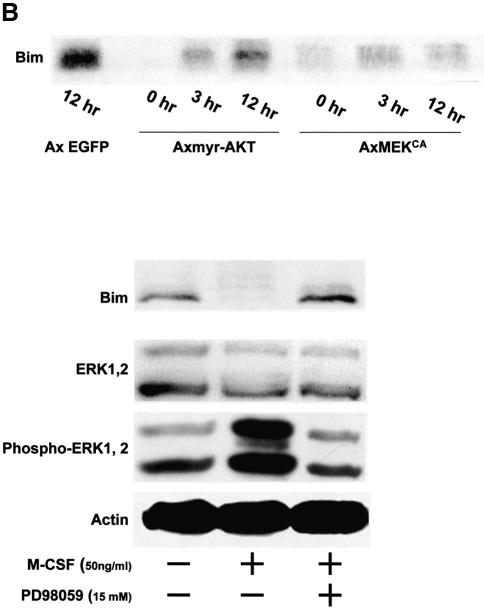
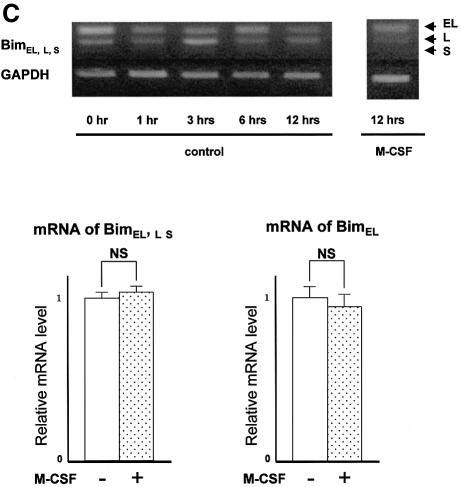
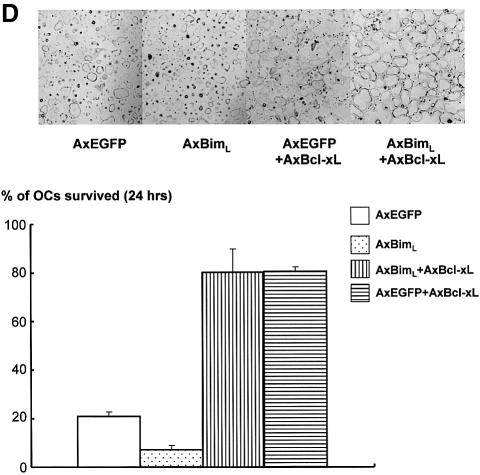
Fig. 1. Regulation of Bim expression in OCs. (A) Cytokine withdrawal caused rapid upregulation of Bim levels in OCs. OCs purified from co-cultures by removing osteoblastic cells by collagenase and dispase treatment were then maintained in the presence of M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for an additional 12 h. The expression levels of Bim and other apoptosis-regulatory proteins in OCs after M-CSF removal were analyzed by western blotting using specific antibodies. Bim levels increased within 3 h, and the upregulation was sustained at least for 12 h. This upregulation of Bim level was strongly suppressed by M-CSF, and to a lesser extent by sRANKL treatment for 12 h. (B) Intracellular signaling pathways leading to Bim downregulation. Upper panel: introduction of MEKCA strongly suppressed the upregulation of Bim after M-CSF removal. Overexpression of myr-Akt had less effect on Bim expression in OCs. Lower panel: treating the cells with a specific inhibitor of MEK/ERK pathways, PD98059, completely abolished the suppressive effect of M-CSF on Bim expression. (C) Transcriptional regulation of bim in OCs. No significant change in the mRNA level of three isoforms of bim, i.e. bimEL, L and S (upper and lower left), or the bimEL specific mRNA level (lower right) was detected in OCs in the presence or absence of M-CSF as determined by RT–PCR (upper) or real-time PCR (lower). The y-axis indicates the relative mRNA levels. NS = not significantly different. (D) Effect of adenovirus vector-mediated overexpression of BimL and/or Bcl-xL on OC survival. Upper panel: TRAP staining. Lower panel: percentage of OCs surviving. Overexpression of BimL promoted apoptosis of OCs (AxBimL). Not only did Bcl-xL overexpression suppress apoptosis of OCs (AxEGFP + AxBcl-xL), but co-expression of Bcl-xL together with BimL completely abrogated the pro-apoptotic effect of BimL (AxBimL + AxBcl-xL).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.