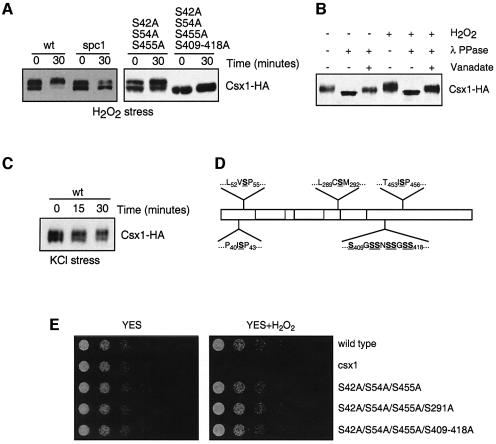
Fig. 3. Csx1 phosphorylation. (A) Wild-type (Csx1-HA) and spc1Δ (spc1Δ Csx1-HA) cultures were treated with 1 mM H2O2 and cells were collected after 30 min. Equal amounts of whole-cell extract were loaded per lane (25 µg). Detection of Csx1-HA was done using monoclonal α-HA antibodies. Mutants S42A/S54A/S455A and S42A/S54A/S455A/S409–418A were treated in the same way. (B) Wild-type cells (Csx1-HA) were treated with 1 mM H2O2 for 30 min, and whole-cell extracts were obtained. After immunoprecipitation with polyclonal α-HA antibodies, the pull-down was treated with λ phosphatase. The resulting reaction was resolved by SDS–PAGE, and Csx1-HA protein was detected by western blot using specific monoclonal α-HA antibodies. (C) Wild-type (Csx1-HA) and spc1Δ (spc1Δ Csx1-HA) cultures were treated with 0.6 M KCl and cells were collected after 15 and 30 min. Equal amounts of whole-cell extract were loaded per lane (25 µg). The detection was done using monoclonal α-HA antibodies. (D) Scheme of Csx1 proteins showing underlined the serine residues mutated to alanine in different mutants. (E) Serial dilutions of wild-type, csx1Δ, csx1-S42A/S54A/S455A, csx1-S42A/S54A/S455A/S291A and csx1-S42A/S54A/S455A/S409-S418A were plated in rich medium (YES) or rich medium with 0.4 mM H2O2 (oxidative stress). Pictures were taken after incubation of the plates for 3–5 days at 30°C.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.