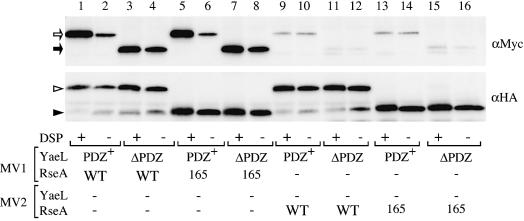
Fig. 3. Crosslinking and co-immunoprecipitation of RseA and YaeL. For lanes 1–8, membrane vesicles carrying indicated combinations of YaeL(H22F)-His6-Myc (shown as PDZ+), YaeLΔPDZ(D402N)-His6-Myc (shown as ΔPDZ), HA-RseA (shown as WT) and HA-RseA165 (shown as 165), were treated with or without DSP. For lanes 9–16, YaeL and RseA were present in separate membrane vesicles (MV1 and MV2), which were mixed and DSP-treated or mock-treated. Membrane proteins were solubilized with 1% N-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside and subjected to immunoprecipitation using immobilized mouse-monoclonal anti-HA antibodies. Proteins recovered were solubilized in SDS, reduced with β-mercaptoethanol to cleave the crosslinkages, and analyzed by SDS–PAGE/immunoblotting using anti-Myc (upper panel) or anti-HA (lower panel) rabbit antibodies. Open arrow, closed arrow, open arrowhead and closed arrowhead indicate YaeL(H22F)-His6-Myc, YaeLΔPDZ(D402N)-His6-Myc, HA-RseA and HA-RseA165, respectively. Direct SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting (without the HA immunoprecipitaiton) demonstrated that all the samples used above contained similar amounts of the YaeL derivatives (not shown).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.