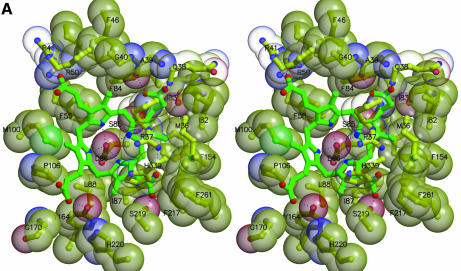
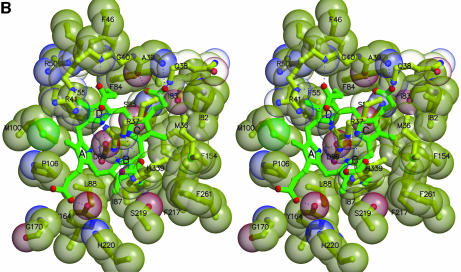
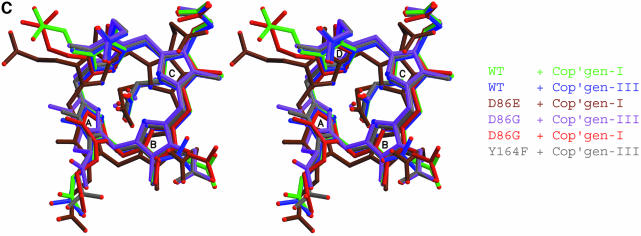
Fig. 3. Interactions at the active site. (A) Uroporphyrinogen I product (green), wild-type URO-D (yellow). Protein residues are shown if one atom from the residue lies within 4.0 Å of the product in at least one of the structures. Also shown is Leu88. The pyrrole rings are denoted A, B, C and D, with the D-ring being the site where acetate and propionate groups are reversed in the III-isomer product. Van der Waals’ surfaces are shown around the protein atoms, with residues nearer the viewer given a more transparent surface. Hydrogen bonds are indicated with dashed lines. The apparent hydrogen bond seen between Ala39 O and the C-ring propionate indicates that this carboxylate is protonated. (B) Same as (A), but for the III-isomer product complex. The I- and III-isomer products superimpose very closely following overlap on the protein Cα atoms. The major differences are the conformations of Arg37 and Arg 41 side chains. (C) Comparison of product bound to various URO-D variants. Structures were superimposed by overlap on the protein Cα atoms. The water molecules that lie roughly in the position of the wild-type Asp86 side chains are shown explicitly. Color scheme is indicated and is the same as in Figure 2B. This figure was generated using Molscript (Kraulis, 1991) and Raster3D (Merritt and Bacon, 1997).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.