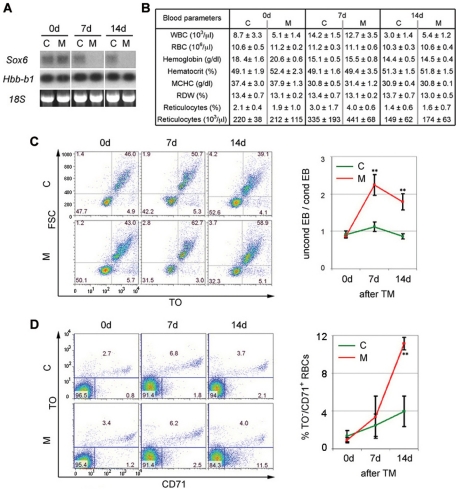
Figure 2. Sox6 is primarily needed for erythroid cell maturation under adult physiological conditions.
(A) Northern blot of bone marrow RNA collected 0, 7 and 14 days after initiation of TM treatment of 10-week-old Sox6fl/fl control (C) and Sox6fl/flCaggCreER mutant (M) mice. Sox6 RNA was detected using a coding-exon-2 probe. Hybridization with an Hbb-b1 probe and staining with ethidium bromide of 18S rRNA are shown as controls for RNA loading. (B) Blood parameters in similar mice as in panel (A). Data are reported as average values with standard deviation obtained for 3 mice per genotype. Other blood parameters measured by the ADVIA instrument and not shown in this table were normal in mutant mice. (C) FACS analysis of erythroblasts in the bone marrow of mice treated as in panel (A). Left, representative FSC/TO FACS profiles of TER119+/CD71+ cells. Right, ratios of uncondensed/condensed erythroblasts. The data are presented as the average with standard deviation of values obtained for 3 mice per genotype. (D) FACS analysis of blood from the same mice as in panel (C). Left, representative TO/CD71 FACS profiles. Right, ratios of atypical reticulocytes (TO−/CD71+). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.