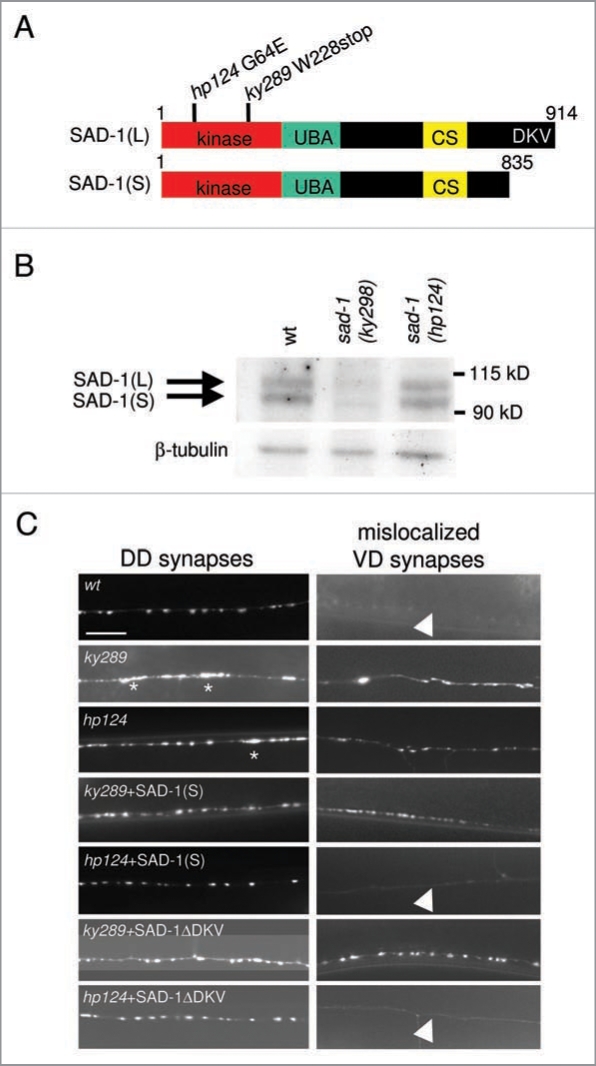
Figure 1.
SAD-1 dimer/oligomerizes. (A) Schematic representations of SAD-1(L) and SAD-1(S) protein structures. Each isoform comprises a kinase domain, ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain, and a unique C-terminal sequence (CS) conserved amongst SAD kinases. In addition, SAD-1(L) has a PDZ domain-binding consensus sequence at the C-terminus (DKV) to which NA B-1 binds. The molecular lesions of two sad-1 mutants, ky289 and hp124, are shown. The ky289 mutation causes an early stop codon whereas hp124 changes a conserved glycine residue in the kinase domain to glutamic acid. (B) Biochemical characterization of sad-1 mutants. SAD-1 protein levels were examined in wild-type, ky289, and hp124 animals by immunoblotting using anti-SAD-1 (top) and anti-β-tubulin for loading control (bottom). While no SAD-1 was detected in ky289 null mutants, both isoforms were detected in hp124 mutants. (C) Differential neuronal phenotype rescues by SAD-1(S) or SAD-1ΔDKV in ky289 and hp124 mutants. Neuronal phenotypes of the GABAergic neurons along the dorsal nerve cord (DN C) were examined using a pre-synaptic vesicle marker, SNB-1::GFP. For synaptic organization, SNB-1::GFP signals in the axons of the DD class GABAergic neurons were examined (left). In wild-type animals, SNB-1::GFP exhibited uniform shape, size, and spacing. Both alleles of sad-1 displayed uneven and diffuse SNB-1::GFP morphology (asterisks) which was fully rescued by either SAD-1(S) or SAD-1ΔDKV. For neuronal polarity, SNB-1::GFP signals mis-localizing to the dendrites of the VD class GABAergic neurons were examined (right). In wild-type animals, no pre-synaptic SNB-1::GFP was mis-localized (arrowhead). In both alleles of sad-1, ectopic SNB-1::GFP signals were observed. This defect was rescued only when SAD-1(S) or SAD-1ΔDKV was expressed in SAD-1(KD)-producing hp124 mutants and not in the protein-null ky289 mutants. Scale bar, 5 µm.