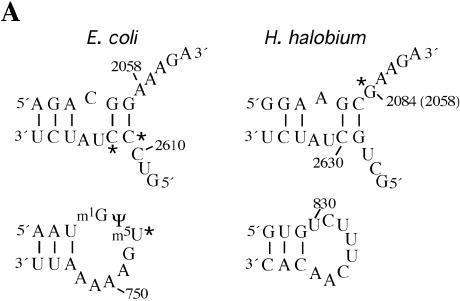
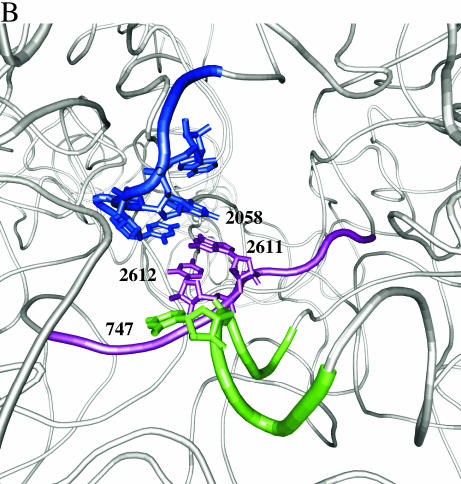
Figure 6.
Chloramphenicol-dependent modification sites on E.coli and H.halobium 23S rRNAs. (A) The modification sites are indicated with asterisks on the secondary structures of relevant portions of 23S rRNA. Segments of domains V (top) and II (bottom) of E.coli (left) and H.halobium (right) 23S rRNAs are illustrated. On the domain V segment of H.halobium 23S rRNA, E.coli numbering is given in parenthesis. (B) The location of chloramphenicol-dependent modification sites on the H.marismortui 50S subunit. The view shown is from the back of the subunit looking through the peptide exit tunnel towards the subunit interface. The coordinates of the H.marismortui 50S subunit are used (PDB accession no. 1JJ2). The positions of the modifications are labeled (using E.coli numbering) and shown in blue (2058), magenta (2611, 2612) and green (747). Other nucleotides in the hydrophobic crevice (13), 2057 and 2059, are depicted in blue. The respective segments of 23S rRNA flanking these nucleotides are depicted as tubes of the same color. Other regions of 23S rRNA are shown as light gray ribbons. This image was made with VMD. VMD is developed with NIH support by the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics group at the Beckman Institute, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/).