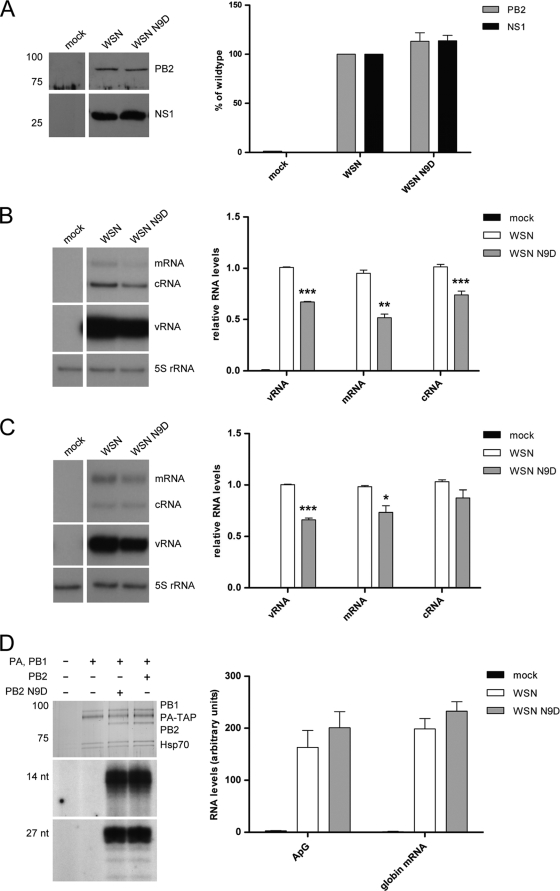
FIG. 7.
Accumulation of viral proteins and RNAs in A549 cells infected with wild-type or PB2 N9D mutant influenza virus and the effect of the N9D mutation on RNA polymerase activity. (A) Western blotting and quantitative analysis of PB2 and NS1 in lysates from A549 cells infected with WSN or WSN N9D at an MOI of 0.3 for 12 h. (B and C) Primer extension analysis of the three viral RNA species of the PB2 (B) and neuraminidase (C) genes in A549 cells infected with WSN or WSN N9D at an MOI of 0.3 for 12 h. Bars represent standard errors of the means based on four independent experiments. ***, P ≤ 0.0004; **, P < 0.005; *, P < 0.03 (based on a paired, two-tailed Student's t test). (D) 293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing PA-TAP and PB1 and either wild-type PB2 or N9D PB2 from A/WSN/33. Cells were lysed at 48 h posttransfection, and proteins were purified by IgG-Sepharose column chromatography. Purified proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained by silver (top panel). In vitro transcription assays were performed with ApG dinucleotide primer (middle panel) or in the presence of globin mRNA as a donor of capped-RNA primer (bottom panel). Transcription products were analyzed by PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. Quantitation of transcription products was done by phosphorimager analysis of experiments performed in triplicate.