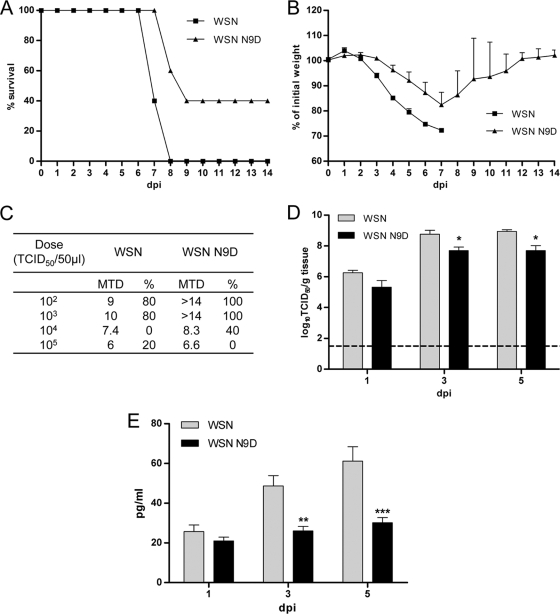
FIG. 8.
WSN N9D virus expressing nonmitochondrial PB2 is attenuated in vivo. (A) Groups of five C57/B6 mice were infected intranasally with 104 TCID50s/50 μl of either WSN or WSN N9D virus. Animals were weighed daily and were euthanized when they lost more than 25% of their weight; percent survival is plotted on the y axis. (B) Weights of infected mice were measured daily and recorded as percentages of initial weight. Mean percent weights on each day are shown. (C) Groups of five C57/B6 mice were infected intranasally with the indicated dose of either WSN or WSN N9D virus. The table shows the mean time to death (MTD) in days and percent survival at each dose (%). (D and E) Groups of four C57/B6 mice were infected intranasally with 104 TCID50s of the WSN or WSN N9D virus, and the lungs were harvested at 1, 3, and 5 dpi. Viral titers (log10 TCID50/g of tissue) were determined on Vero 76 cells (D). The dashed line represents the limit of detection (101.5 TCID50s/g). Columns represent mean viral titers. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. *, P < 0.05, based on a Mann-Whitney test. (E) IFN-β was measured using a mouse IFN-β ELISA kit. Columns represent mean observed concentrations of cytokines from four mice. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (two-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni posttest correction).