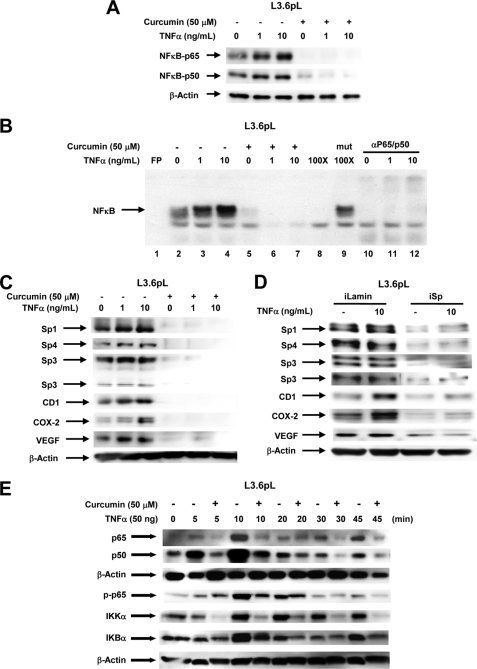
FIGURE 4.
Role of Sp proteins in curcumin-dependent inhibition of TNFα inducible responses in L3.6pL pancreatic cancer cells. A, curcumin decreases TNFα-induced expression of p65 and p50 proteins. Cells were treated with TNFα in the presence or absence of 50 μm curcumin, and nuclear lysates were examined for expression of p65 and p50 proteins by Western blots as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, curcumin decreased TNFα-induced NFκB oligonucleotide-protein binding. L3.6pL cells were treated with DMSO or 50 μmol/liter of curcumin in the presence or absence of TNFα for 24 h, and nuclear extracts were incubated with 32P-labeled NFκB oligonucleotide alone or in the presence of other factors. Retarded bands were analyzed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Effects of curcumin (C) and iSp (D) on Sp/NFκB-dependent protein expression are shown. L3.6pL cells were treated with 50 μm curcumin (C) or transfected with iSp (D) in the presence or absence of TNFα, and whole cell and nuclear lysates were analyzed for Sp1, Sp3, Sp4, p65, p50, CD1, COX-2, and VEGF proteins by Western blot analysis as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The gels were typical of results of at least two replicate determinations per treatment group. E, effects of curcumin on TNFα-induced responses. L3.6pL cells were treated with curcumin or TNFα alone or in combination for up to 45 min, whole cell lysates were obtained and analyzed by Western blots as described under “Experimental Procedures.”