FIGURE 4.
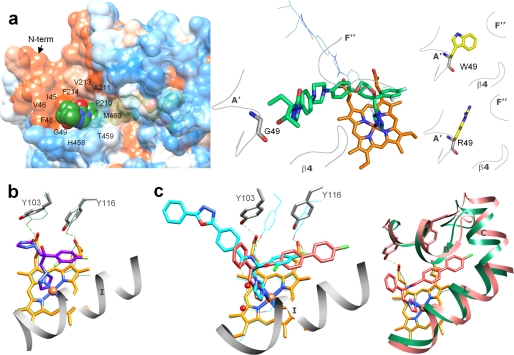
Specific features in the binding of inhibitors. a, the long arm of posaconazole is extended above the protein surface forming 12 additional interactions around the access channel entrance (left panel). The surface is colored by hydrophobicity (from blue for the most polar to white to orange red for the most hydrophobic residues; the surfaces for the three TC14DM structures can be seen as supplemental Fig. S3). Right panel, posaconazole in the TC14DM structure (stick representation) superimposed with its energy-minimized model (line representation). Location of Gly49 in the structure and models of its mutations to the residues found in the posaconazole-resistant A. fumigatus 14DM are shown. b, fluconazole alters positions of conserved Tyr103 and Tyr116 affecting their hydrogen bonding with the heme propionates (rings A and D). The corresponding tyrosines and the heme in the superimposed posaconazole bound TC14DM structure are shown as green lines; the hydrogen bonds are depicted as dotted lines. c, VNF (salmon) binds to TC14DM in the orientation opposite to that of its scaffold analog VNI (cyan) in the Tbb14DM structure. Two water molecules (Tbb14DM) are displayed as red spheres (left panel). Right panel, the longer arm of VNF is intercalated between the B′ helix/B′C loop, helix C, and N-terminal (N-term) part of helix I, slightly broadening the active site cavity. The corresponding structural elements in the superimposed posaconazole-bound TC14DM are colored in green.