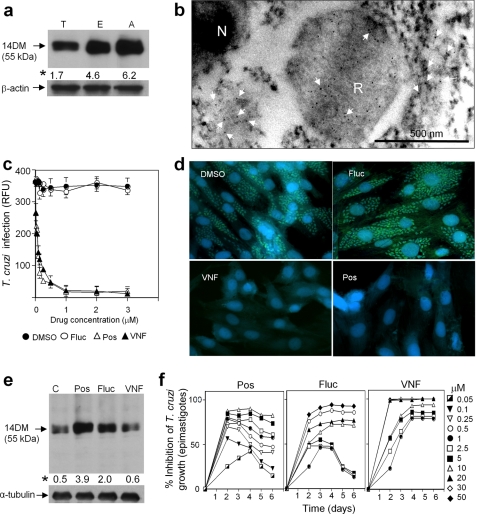
FIGURE 5.
14DM expression, cellular localization, and inhibition in T. cruzi. a, immunoblot analysis of 14DM expression in different life stages of the parasite. Equal concentrations of whole cell extracts of trypomastigotes (T), epimastigotes (E), and amastigotes (A) were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted onto nitrocellulose, probed with mouse anti-Tbb14DM antiserum, and densitometrically scanned. The values (indicated by an asterisk) correspond to relative intensities normalized to the β-actin loading control. b, localization of 14DM in T. cruzi by immunogold electron microscopy. 14DM (arrows) is seen in the cytoplasm and reservosomes (R). N, nucleus. c, inhibition of the ability of trypomastigotes to infect cardiomyocytes by fluconazole (Fluc), posaconazole (Pos), and VNF. GFP-expressing trypomastigotes were pretreated with 14DM inhibitors and exposed to cardiomyocytes monolayers, and infected monolayers were incubated for 72 h to assay for parasite multiplication. The infection was evaluated by GFP fluorescence (RFU). The data represent the mean ± S.D. of the results from triplicate samples. d, fluorescence microscopic observation of the inhibition of T. cruzi multiplication by 1 μm 14DM inhibitors within cardiomyocytes. GFP-expressing amastigotes are seen as small green spots inside cardiomyocytes, and cardiomyocytes nuclei are blue. e, 14DM expression upon exposure of T. cruzi to azole inhibitors. Epimastigotes (106 organisms/ml) were allowed to grow for 5 days after exposure to inhibitors. 14DM expression was analyzed as in a, the values (indicated by an asterisk) were normalized to α-tubulin. f, dose-dependent inhibition of T. cruzi epimastigotes multiplication by 14DM inhibitors. The data represent the mean ± S.D. of the results from triplicate samples.