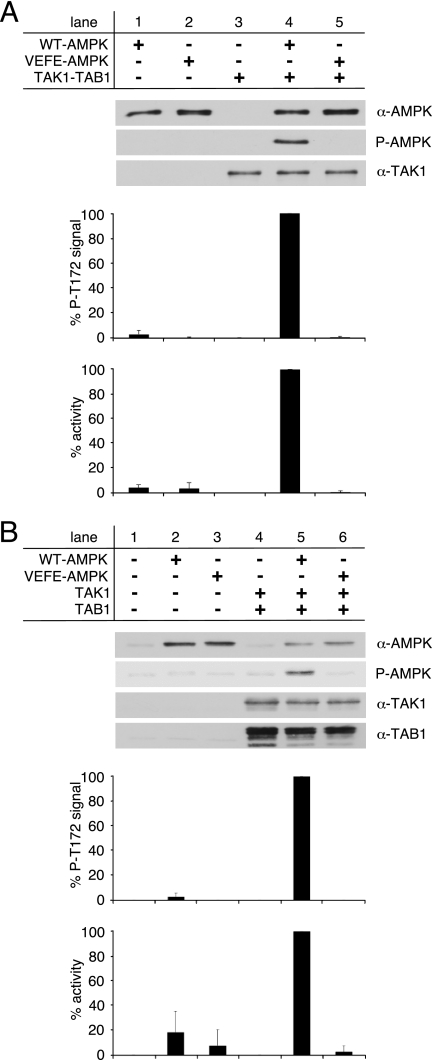
FIGURE 3.
Activation of WT- and VEFE-AMPK by active TAK1. A, in vitro activation of recombinant WT- and VEFE-AMPK by bacterially expressed and purified TAK1-TAB1. Western blot analysis was performed using anti-TAK1, anti-AMPKα, and phospho-specific anti-AMPKα Thr-172 (P-AMPK) antibodies. TAK1 background signal (lane 3) was subtracted, and AMPKα phospho-Thr-172 signal intensities were standardized to AMPKα signals. Activity was determined by a HPLC- and SAMS-peptide-based activity assay. Background signal of TAK1 was subtracted, and data were normalized to WT-AMPK activation by TAK1-TAB1 (n = 3; S.D.). B, HeLa cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-AMPKα1 wild-type and VEFE mutant, FLAG-TAK1, and HA-TAB1. Cells were treated with 1 mm hydrogen peroxide for 15 min before lysis. HeLa cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-TAK1, anti-TAB1, anti-AMPKα, and phospho-specific anti-AMPKα Thr-172 (P-AMPK) antibodies. Subsequent to immunoprecipitation using anti-AMPKα1 antibodies, AMPK activity was determined. Respective background signals from mock- and TAK1/TAB1-double transfected cells were subtracted, and data were normalized to the WT-AMPK/TAK1/TAB1 triple-transfected cells (n = 3; S.D.).