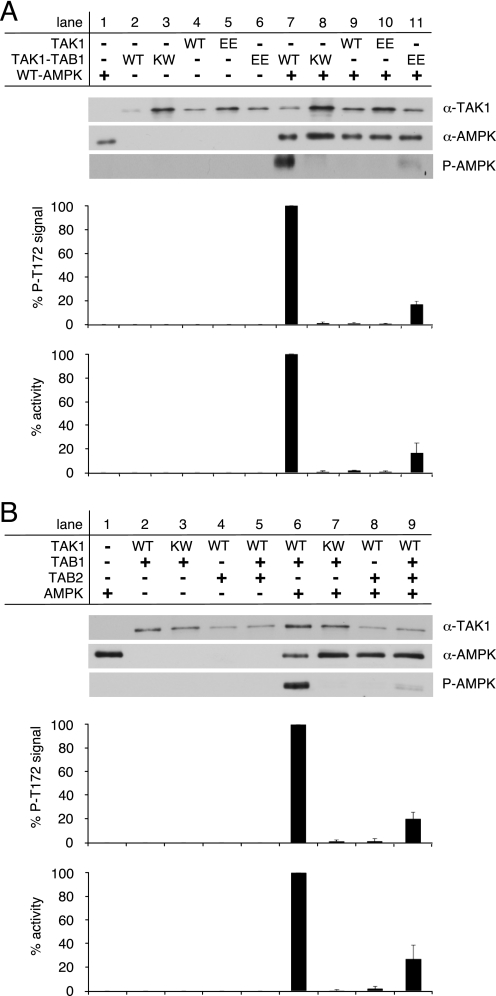
FIGURE 4.
Activation of TAK1 requires co-expression of TAB1. A, recombinant WT-AMPK was activated by bacterially expressed TAK1 and TAK1 co-expressed with TAB1 (TAK1-TAB1). Here, the activities of wild-type TAK1 proteins were additionally compared with the activities of TAK1 proteins carrying the phosphorylation site mimicking mutation T178E,T184E (EE) within the TAK1 activation segment. B, activity of recombinant TAK1 bacterially co-expressed with TAB1 and/or TAB2. The kinase-deficient mutant TAK1(K63W)-TAB1 (KW) served as a control. Western blot analysis utilized anti-TAK1, anti-AMPKα, and phospho-specific anti-AMPKα Thr-172 (P-AMPK) antibodies. The AMPKα phospho-Thr-172 signals were quantified after subtraction of respective WT-AMPK (lane 1) and TAK1 background signals (lanes 2–6) and normalization to AMPKα and TAK1 signals. Activity was determined, and respective background activities were subtracted. All activities were standardized to corresponding TAK1 signal intensities as revealed from densitometric Western blot analysis. The data were normalized relative to WT-AMPK activation by WT-TAK1-TAB1 (n = 3; S.D.).