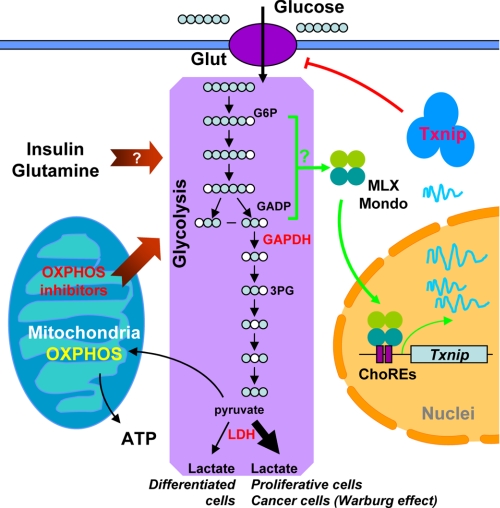
FIGURE 8.
A model linking Txnip expression, glucose transport, glycolysis, OXPHOS, and other physiological cues. OXPHOS inhibitors (this work), glutamine (22), and insulin signaling (9) have all been shown to repress Txnip expression; these factors are also known to increase the glycolytic rate. The augmented glycolytic flux may dynamically deplete glycolytic intermediate metabolites normally involved in transmitting glucose signaling to Mondo-MLX activation, which in turn represses Txnip expression. Our data suggest that the metabolites upstream of the GAPDH enzyme, G6P and GADP in particular but others are not ruled out, are candidates that link Txnip expression to glycolytic flux. How Mondo-MLX transcription factors are activated, the nuclear translocation included, and whether the above mentioned relevant metabolites are directly involved in this activation process are a challenging problem to be addressed in the future. Txnip has an inhibitory role on glucose transport; hence, glucose uptake in cells with repressed Txnip expression will be induced, a common theme in many cancerous cells that are addictive to glucose. Glut, glucose transporters; 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate.