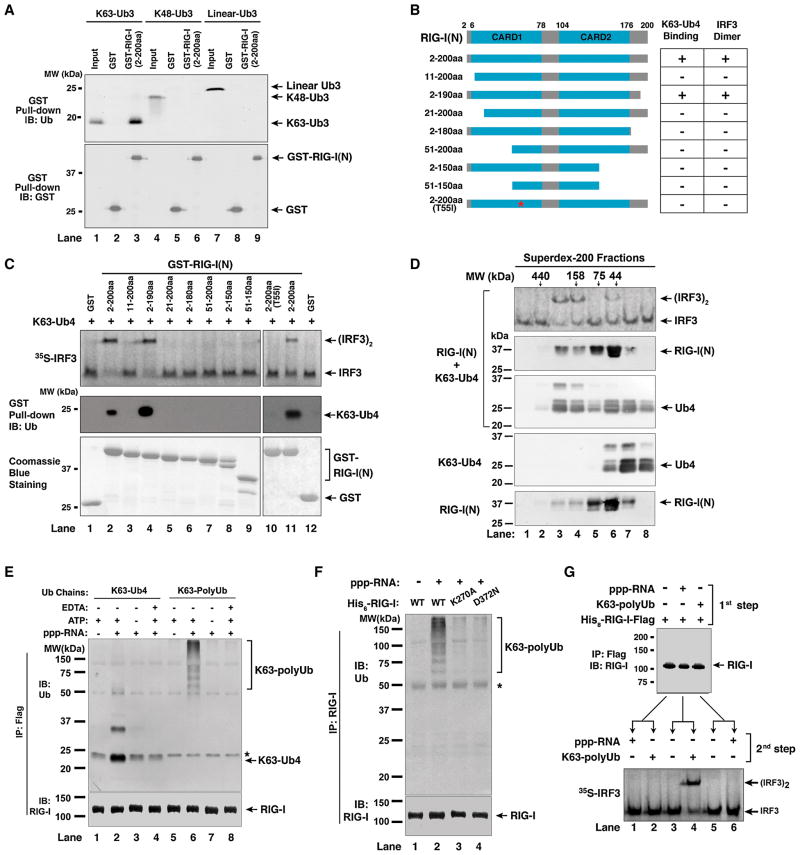
Figure 5. RIG-I CARD Domains Bind K63 Ubiquitin Chains and This Binding in Full-Length RIG-I is Regulated by RNA and ATP.
(A) RIG-I(N) binds specifically to K63 ubiquitin chains. GST or GST-RIG-I(N) was incubated with Ub3 containing K63, K48, or linear linkage, then pulled down with glutathione-Sepharose, followed by immunoblotting. Input represents 10% of Ub3 used in the pull-down experiments. (B) Diagram of RIG-I N-terminus containing the tandem CARD domains and various deletion and point mutants. The table on the right summarizes the results in panel C. (C) Both CARD domains of RIG-I are required for polyUb binding and IRF3 activation. GST-RIG-I(N) and various mutants were incubated with K63-Ub4. 1-μl aliquot of each mixture was used for IRF3 dimerization assay (upper panel), and the remainder was pulled down with glutathione-Sepharose followed by immunoblotting with a Ub antibody (middle panel). The GST-RIG-I(N) and the mutant proteins (2 μg each) were analyzed by Coomassie Blue staining (lower panel). See also Figure S5. (D) RIG-I(N) and K63-Ub4 form active high molecular weight complex. RIG-I(N) was incubated with K63-Ub4 and then the mixture was fractionated on Superdex-200. Aliquots of the fractions were assayed for their ability to stimulate IRF3 dimerization, whereas other aliquots were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against RIG-I and ubiquitin, respectively. K63-Ub4 or RIG-I(N) alone was also analyzed by gel filtration on the same column (lower two panels). (E) Full-length RIG-I binds to ubiquitin chains in a manner that depends on 5′-pppRNA and ATP. His8-RIG-I-Flag was incubated with K63-Ub4 or K63-polyUb chains in the presence or absence of 5′-pppRNA (135nt), ATP or EDTA. Following immunoprecipitation with a Flag antibody, the precipitated proteins were detected with an antibody against Ub or RIG-I. The asterisk indicates a non-specific band. (F) Similar to (E), except that RIG-I ATPase mutants (K270A and D372N) were also tested for binding to K63 polyUb chains. The asterisk indicates a non-specific band. (G) Sequential binding of RIG-I to RNA and polyUb leads to IRF3 activation. His8-RIG-I-Flag was incubated with 5′-pppRNA or K63-polyUb in the first step, then immunopurified using a Flag antibody. The purified RIG-I was incubated with K63-polyUb or 5′-pppRNA in the second step, followed by IRF3 dimerization assay.