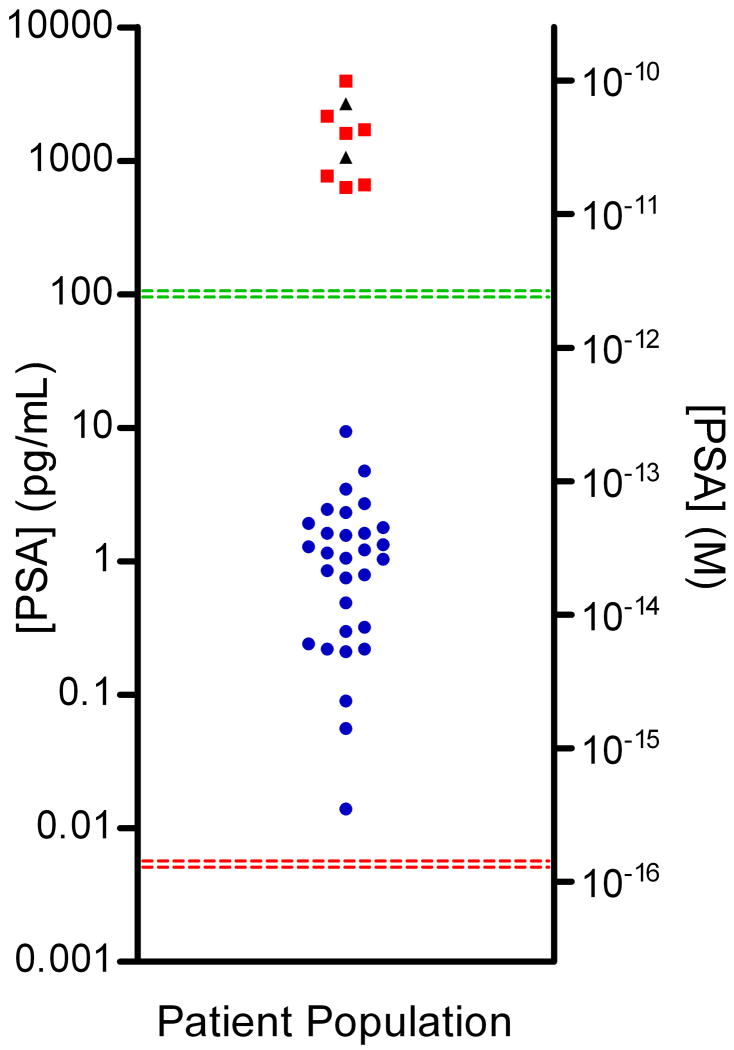
Figure 4. Digital detection of PSA in serum samples of patients who had undergone radical prostatectomy.
Concentrations of PSA in serum samples from RP patients ( ), healthy control samples (
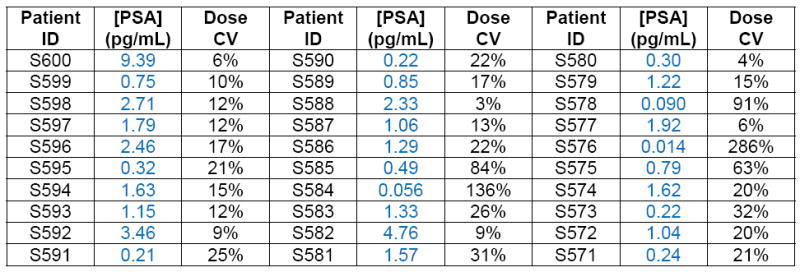
), healthy control samples ( ), and Bio-Rad PSA control samples (▲) determined using digital ELISA. RP patient samples (SeraCare Life Sciences, Milford, MA) all had undetectable PSA levels as measured by a leading clinical diagnostic assay (ADVIA Centaur); the green line represents the detection limit of the ADVIA Centaur PSA assay (100 pg/mL or 3 pM). All 30 patient samples were above the detection limit of the PSA digital ELISA, shown by the red line (0.006 pg/mL or ~200 aM), with the lowest patient PSA concentrations measured at 0.014 pg/mL (~400 aM) using digital ELISA. Patient samples with the lowest PSA levels were detectable, but approached the LOD of the assay resulting in a large imprecision in the concentration determined (high dose %CV). The digital ELISA was validated for specificity to PSA using control standards (Bio-Rad) and serum from healthy individuals (ProMedDx) that had been assayed using the ADVIA Centaur PSA assay (See Supplementary Table 3).
), and Bio-Rad PSA control samples (▲) determined using digital ELISA. RP patient samples (SeraCare Life Sciences, Milford, MA) all had undetectable PSA levels as measured by a leading clinical diagnostic assay (ADVIA Centaur); the green line represents the detection limit of the ADVIA Centaur PSA assay (100 pg/mL or 3 pM). All 30 patient samples were above the detection limit of the PSA digital ELISA, shown by the red line (0.006 pg/mL or ~200 aM), with the lowest patient PSA concentrations measured at 0.014 pg/mL (~400 aM) using digital ELISA. Patient samples with the lowest PSA levels were detectable, but approached the LOD of the assay resulting in a large imprecision in the concentration determined (high dose %CV). The digital ELISA was validated for specificity to PSA using control standards (Bio-Rad) and serum from healthy individuals (ProMedDx) that had been assayed using the ADVIA Centaur PSA assay (See Supplementary Table 3).