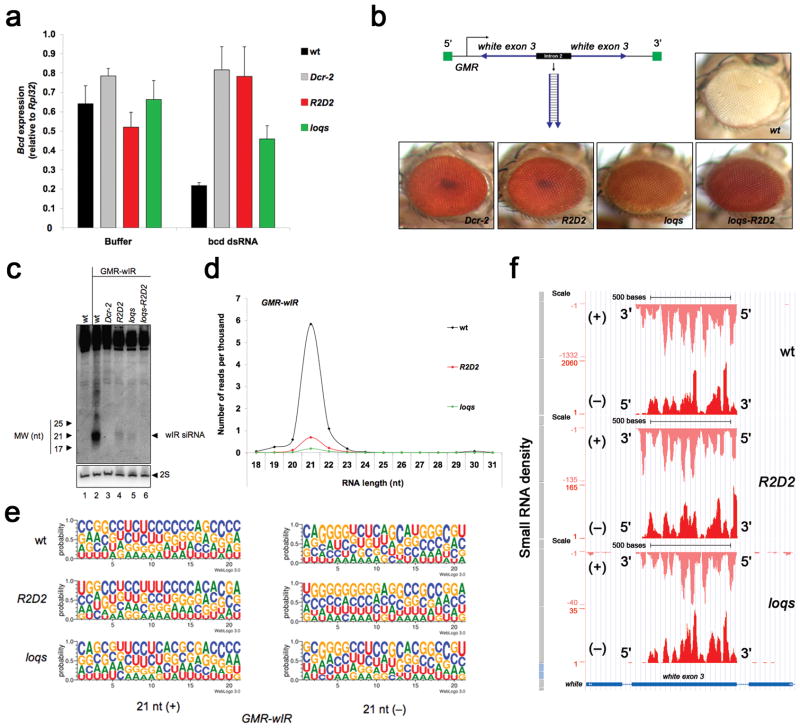
Figure 1. R2D2 and Loqs are required for silencing triggered by dsRNA from endogenous or exogenous sources.
(a) Silencing of the bcd gene triggered by injection of dsRNA into embryos, as assessed by RT-qPCR analysis of bcd mRNA. RNA was extracted 1.5 h post-injection, and buffer injected embryos were used as controls. The graph displays the mean and standard deviation (n=3). (b) Silencing of the white gene triggered by the GMR-wIR transgene (detail in the figure), as assessed by eye color. (c) Detection of GMR-wIR-derived siRNA by Northern blotting of small RNA fractions from heads. 2S rRNA blotting was used as a loading control. (d) Size distribution and normalized number of sequenced RNAs derived from GMR-wIR. (e) Sequence logo plots of 21-nt sense (+) and antisense (−) RNAs sequenced from GMR-wIR. The height of symbols within the stack indicates the relative frequency of each nucleotide at that position in all GMR-wIR RNAs. The RNAs are oriented such that the 5′ end is to the left. (f) Small RNA density along the region of the white gene that matches GMR-wIR, as provided by the UCSC Genome Browser. Note the different scales used for plotting the small RNA density in wildtype, R2D2 and loqs mutants to allow for comparison of the relative cover-age. The density of sense (+) and antisense (−) small RNAs, and the 5′ and 3′ ends of the two strands are shown.