Figure 6. Stable Presence of HSP26 mRNAs Within PBs Requires Igo1 and Igo2.
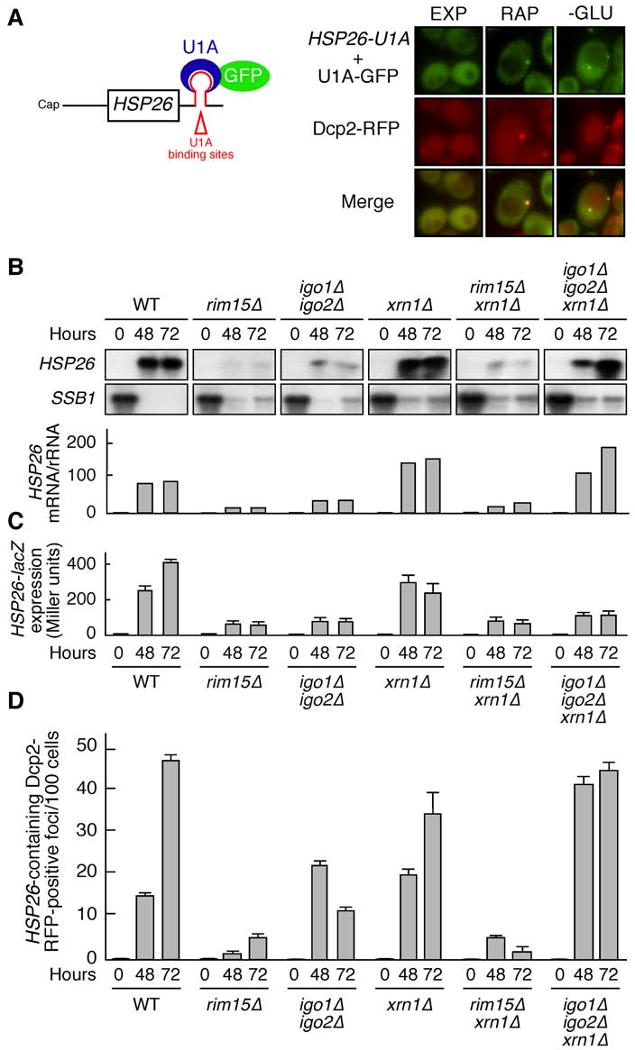
(A) HSP26 mRNA co-localizes with the PB marker Dcp2-RFP. Binding of U1A-GFP to an HSP26 mRNA harboring multiple (16 in total) U1A binding sites in its 3′ UTR allows analysis of HSP26 mRNA localization. Wild-type cells co-expressing Dcp2-RFP, as well as HSP26-U1A mRNA and U1A-GFP were harvested prior to (EXP), or following rapamycin treatment (RAP; 0.2 μg ml-1; 2 hr), or glucose limitation (i.e. following growth for 24 hr in batch cultures; -GLU) and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. GFP foci were absent in control cells expressing either the HSP26 reporter or the U1A-GFP fusion plasmid solely (Hoyle et al., 2007); and data not shown).
(B) Loss of Xrn1 suppresses the defect of igo1Δ igo2Δ, but not that of rim15Δ cells, in HSP26 mRNA expression following glucose limitation. Northern analyses of HSP26 and SSB1 in wild-type and indicated mutant strains harvested in exponential growth phase (0) and following glucose limitation (i.e. following growth for 48 hr or 72 hr in batch cultures). All samples were run on the same gel (identical film exposure time). Bar graphs show the relative levels of HSP26 mRNA per rRNA (arbitrarily set to 1.0 for exponentially growing wild-type cells).
(C) Loss of Xrn1 does not suppress the defect of igo1Δ igo2Δ in HSP26-lacZ expression following glucose limitation. HSP26-lacZ expression was monitored (as in Figure 2D) in wild-type and indicated mutant strains that were grown as in (B). In control experiments, HSP26-lacZ mRNA accumulation patterns were found to be comparable to the ones of the endogenous HSP26 gene for all strains studied (data not shown).
(D) Igo1/2 ensure survival of HSP26 mRNAs within PBs. The number of HSP26 mRNA-containing, Dcp2-RFP-positive cytoplasmic foci per 100 cells was determined (as in [A]) in wild-type and indicated mutant strains that were harvested in exponential growth phase (0) and following glucose limitation (i.e. following growth for 48 hr or 72 hr in batch cultures). Data are reported as averages (n = 3), with SDs indicated by the lines above the bars. Please note that Igo1/2 are dispensable for translation per se (Figure S4).
