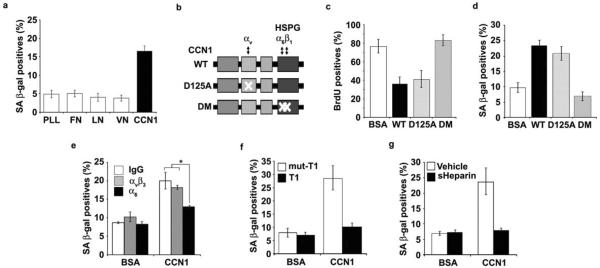
Figure 3. CCN1 induces senescence through integrin α6β1-HSPGs.
(a) Cells were adhered to dishes coated with ECM proteins including fibronectin (FN; 10 μg/ml), vitronectin (VN; 5 μg/ml), laminin (LN; 1 μg/ml), CCN1 (5 μg/ml) and poly-L-Lysine (PLL; 10 μg/ml), and stained for SA-β-gal after 3 days. (b) Schematic diagram of CCN1 showing the domain structure and the D125A30 and DM26 mutants, which are disrupted in binding sites for αv and α6β1-HSPG, respectively. (c) Cells were treated with either WT or mutant CCN1 proteins (2.5 μg/ml each) for 3 days and subjected to BrdU incorporation assay, and (d), SA-β-gal assay. (e) Cells were pre-incubated with function-blocking mAbs (50 μg/ml) against αvβ3 (LM609) or α6 (GoH3), and assayed for SA-β-gal. (f) Cells were treated with CCN1 with either the α6β1-binding T1 peptide or the non-binding mutant (mut-T1; 0.5 mM each)27, 33 as a competitor, and SA-β-gal measured. (g) soluble heparin (1 mg/ml) was added 1 h before CCN1 treatment, and SA-β-gal assayed. Experiments were done in triplicates and data presented as means ± S.D. (*p<0.004).