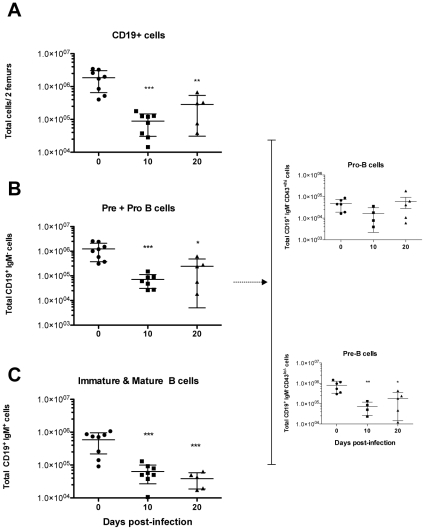
Figure 5. T. vivax infection leads to elevated bone marrow dynamics and alterations in the maturation of B-cell progenitors.
Mice were infected i.p. with 102 bloodstream forms of T. vivax. Pools of bone marrow cells were obtained from both femurs of four to eight 8-week-old outbred mice then analyzed per animal at 10 and 20 d.p.i. by immunofluorescence and compared with bone marrow cells from normal age-matched uninfected controls. Cells were stained for IgM, CD19 and CD43, and SSC-A/FCS-A combined plots were used to gate lymphocyte populations. Doublets were eliminated by a FSC-W/FSC-H combined gate (see Figure S3, for gating strategy). CD19+ cells were gated and total numbers of positive cells per 2 femurs are depicted in (A); PreB + Pro B (CD19+IgM−) and late immature/mature B (CD19+IgM+) cell numbers are shown respectively in (B) and (C); total numbers of Pro-B and Pre-B cells (B, right panel) were deduced from the expression of CD43 by CD19+IgM− Pre B + Pro B gated cells. Results are expressed per individual mouse and are representative of at least 3 different experiments per time point. Arithmetic means ± SD of the means are presented. * p<0.05, ** p<0.001, *** p<0.0001 cell when compared with samples from day 0.