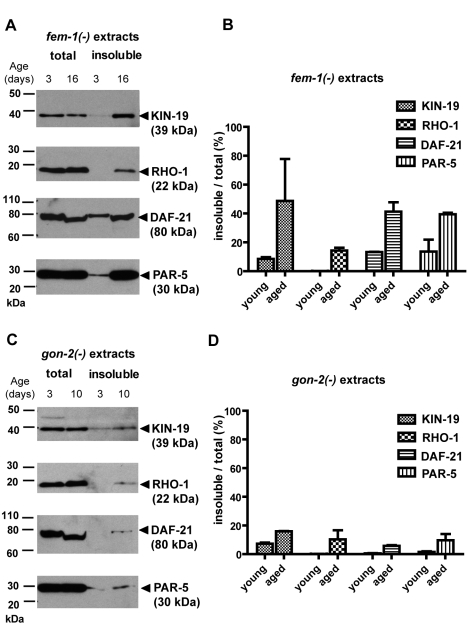
Figure 3. Insoluble but not total levels of four aggregation-prone proteins increased with age.
(A and C) Western blot detection of KIN-19 (CK1α), RHO-1, DAF-21 (Hsp90), and PAR-5 (14-3-3) in young and aged animals containing either somatic and germline tissue [fem-1(−), (A)] or containing only somatic tissues [gon-2(−), (C)]. The total fraction (Urea and SDS buffer) contains all proteins and the detergent-insoluble fraction contains aggregation-prone proteins. The total protein fraction was diluted 1∶3 compared to insoluble fraction. Arrowheads mark the protein bands corresponding to the aggregation-prone candidates. Overall, Western blot analysis confirms our mass spectrometry results demonstrating a large increase in insolubility with age. With age, we noted a slight decrease in the size of full-length DAF-21 (less than 10 kDa). (B and D) Quantification of the fractional increase in aggregated levels compared to total levels of each candidate evaluated by Western blot. These results demonstrate that age-dependent insolubility for each of the four proteins we examined occurs independently of an increase in total protein levels. Extracts from two biologically independent experiments were evaluated. Error bars indicate SEM.