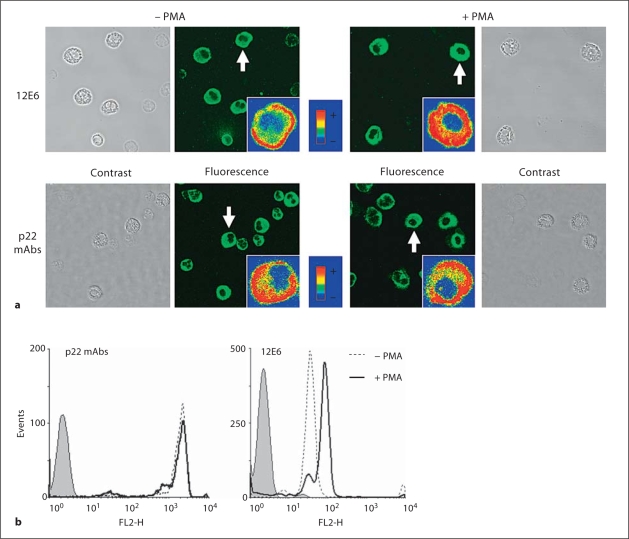
Fig. 8.
Immunological analysis of cytochrome b558 activation ex vivo. a Detection of p22-phox in resting and PMA-stimulated neutrophils by confocal microscopy. Neutrophils were incubated with PMA (130 nM) or DMSO for 10 min at 37°C. Resting and stimulated cells (2 × 105 cells) were then fixed, permeabilized and labeled with anti-p22-phox mAbs (5 μg) for 1 h at room temperature as described in Materials and Methods. An Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody was used to detect the mAb binding. Inserts show typical cells (indicated by a white arrow) in false colors for the sake of comparison of fluorescence levels. Phase contrast, differential interference contrast and fluorescence images were recorded. b Flow cytometry analysis of cytochrome b558 in resting and PMA-stimulated neutrophils. Purified human neutrophils (5 × 105 cells) were stimulated (plain line) or not (dotted line) with 130 nM PMA for 10 min at 37°C, washed, fixed with 1% (w/v) paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.01% (w/v) saponin and labeled with specific mAbs, 12E6 mAb or other p22-phox mAbs (17A2, 16G7, 16G6, 13D4 or 13C4; 5 μg; dotted and plain lines) or irrelevant mAb (5 μg; grey area) for 30 min on ice. The antibodylabeled cells were stained with PE-conjugated secondary antibody, and the fluorescence (FL2) was measured.