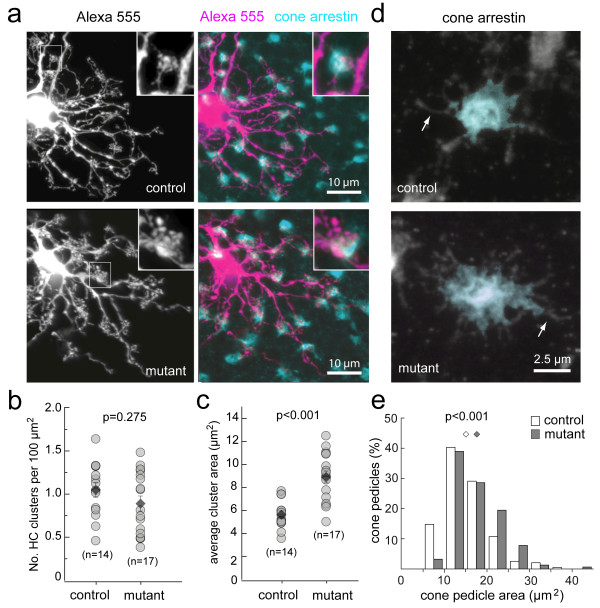
Figure 7.
Horizontal cell dendritic cluster area and cone pedicle size are significantly increased in the mutant retina. (a) Examples of horizontal cells in P10 littermate control and mutant retinas that were intracellularly dye-filled with Alexa Fluor 555. Mutant retinas were immunostained for GAD67 to determine whether cells were located in the wild-type or knockout regions (not shown). Insets show dendritic terminal clusters that overlay cone pedicles (revealed by immunostaining for cone-arrestin) at their sites of contact. (b,c) Quantification of horizontal cell (HC) terminal cluster density (number of clusters per 100 μm2 dendritic field area) and average cluster area per cell. n = number of retinas. Filled diamond and error bar = mean and standard error. (d) High magnification examples of the maximum intensity projections of an image stack through a cone pedicle in a littermate control retina and a pedicle in the mutant retina. Colored regions within the cone pedicles mark the cone pedicle 'area' determined from their respective labeled-fields (see Materials and methods). Arrows indicate an example of filopodia that decorate the base of the cone pedicles. (e) Distributions of cone pedicle areas in littermate control and mutant retinas. Diamonds indicate means of the distributions: mutant (17.15 ± 0.46 μm2), n = 154 pedicles, n = 4 animals; control (15.20 ± 0.38 μm2), n = 196 pedicles, 5 animals.