Figure 1.
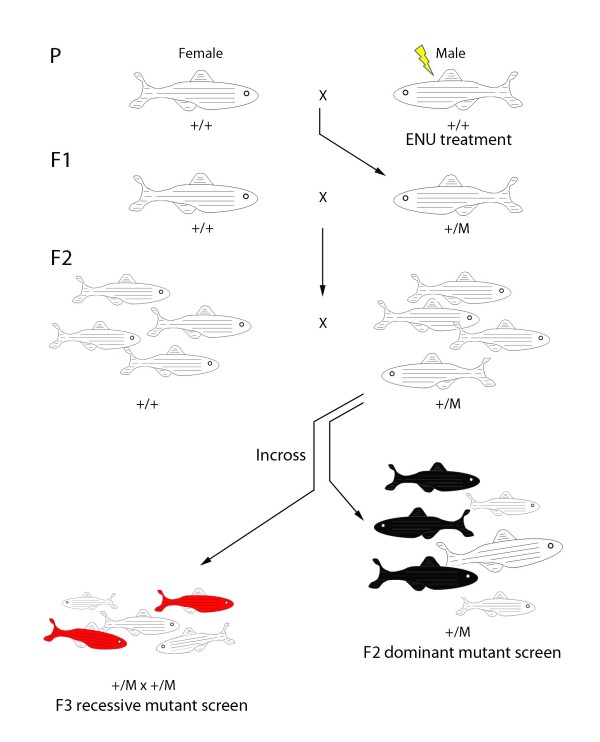
Three-generation breeding scheme for chemically-induced mutant fish. Male fish are mutagenised and then crossed to wild-type females to produce an F1 generation. An F2 generation is made by in-crossing F1 siblings. Dominant behavioural mutants can be identified in this F2 generation (black fish). For recessive mutant carriers, a second in-cross is performed and the progeny screened for behavioural alterations (red fish) - if the inheritance in Mendelian then one quarter of the progeny should show the behavioural defect.
