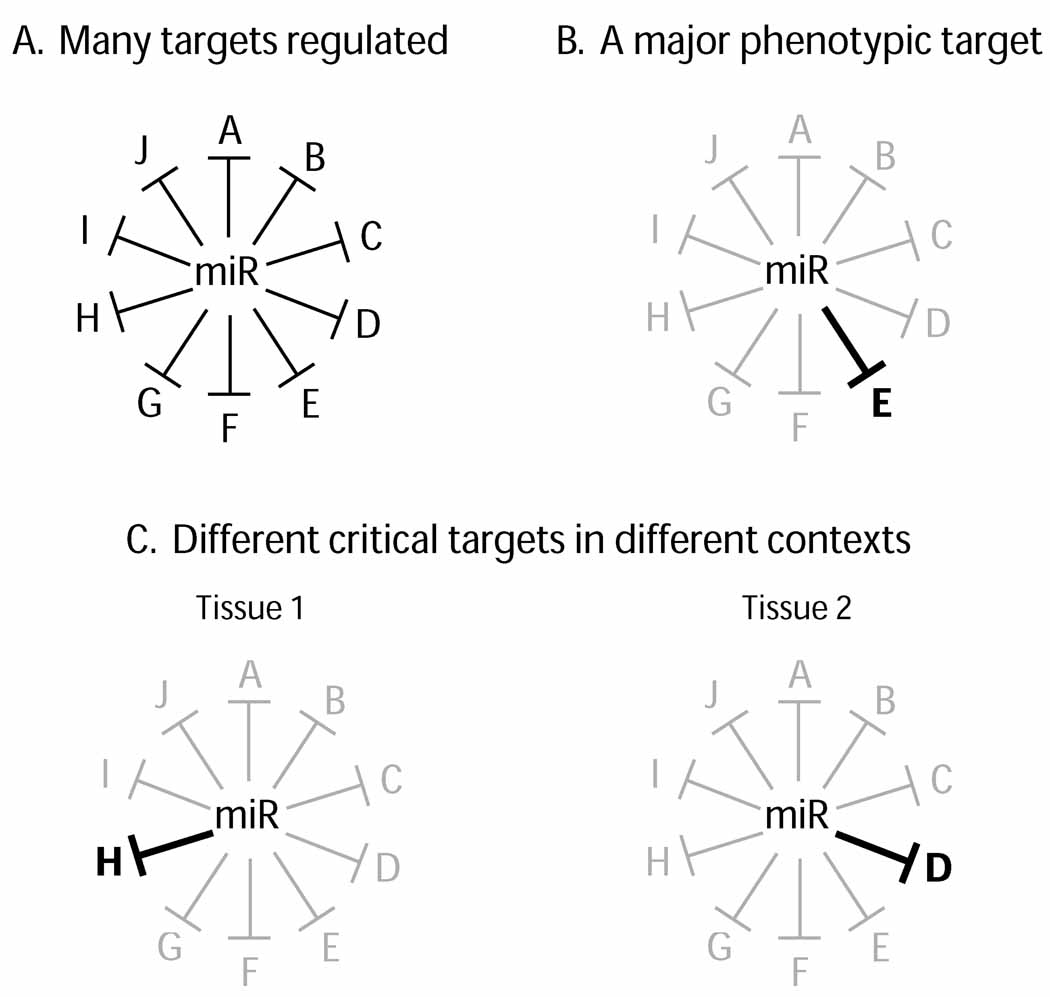
Figure 1. Modes of miRNA regulation.
(A) Individual miRNAs often regulate many targets, each of which may contribute subtly to the overall biological function of the miRNA. (B) A miRNA may repress a large network of targets, but the regulation of a specific target may underlie the major phenotypically visible role of the miRNA. Note that this does not necessarily mean that it is quantitatively the most strongly repressed target of the miRNA; depending on the function of the target, a relatively modest change in activity might elicit a mutant phenotype. (C) A miRNA may function in multiple spatial or temporal contexts, and may have different critical targets in each setting.