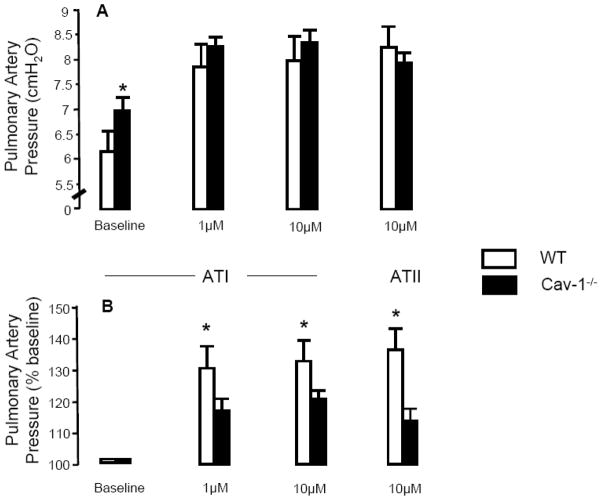
Figure 4. Effect of AI Infusion on Pulmonary Artery Pressure in the Isolated Perfused Mouse lung.
Pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) was measured in isolated buffer-perfused and ventilated mouse lung preparations (flow rate = 2.0 ml/min) at baseline and following infusion of angiotensin I (ATI) and angiotensin II (ATII). Data presented in panel A are absolute PAP values in cmH2O and in panel B are as percent change from baseline following infusion of ATI and ATII. PAP at baseline was significantly increased (by 15%) in Cav1−/− lungs compared to WT (A). Infusion of 1 μM and 10 μM ATI increased PAP in both groups (A, B), but the response was attenuated in Cav1−/− lungs (A, B). Infusion of 10μM ATII also raised PAP to a greater extent in WT lungs compared to Cav1−/− lungs (A, B) (*p<0.05, n=3–4).