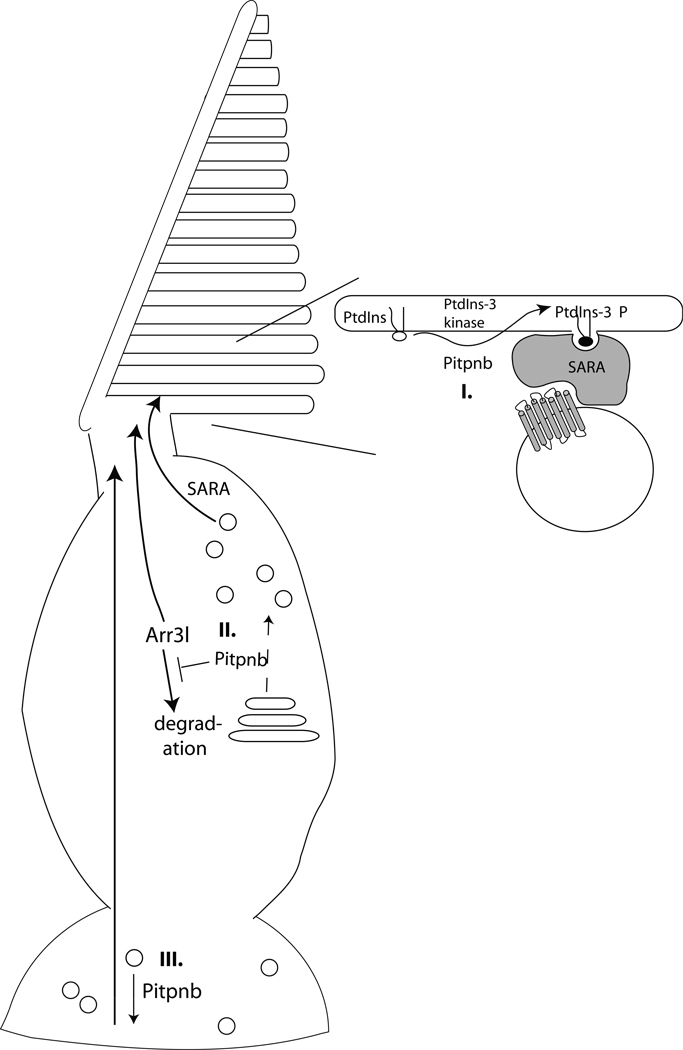
Fig. 10.
Pitpnb function in double cone cell outer segment biogenesis and maintenance. (I) Pitpnb cooperates with a PtdIns 3-OH kinase to promote PtdIns-3-phosphate production on the outer segment. PtdIns-3-phosphate serves as a landmark on the outer segment membrane that facilitates SARA-regulated docking and fusion of opsin-containing vesicles to the outer segment (acceptor compartment). (II) Pitpnb cooperates with what would likely be a PtdIns 4-OH kinase, at the level of the double cone cell Golgi complex, to promote formation of opsin-containing vesicles that will ultimately fuse to outer segment discs in a SARA-regulated manner. (III) Pitpnb regulates signaling in the synaptic pedicle and the robustness of this signaling is transduced from the synaptic pedicle to outer segments. In this model, Pitpnb may promote formation/fusion of synaptic vesicles and, in the absence of proper synaptic signaling, the outer segment of the cone cell is not maintained. In all three scenarios, Arr3L protein stability is suggested to be dependent on its association with functional outer segments.