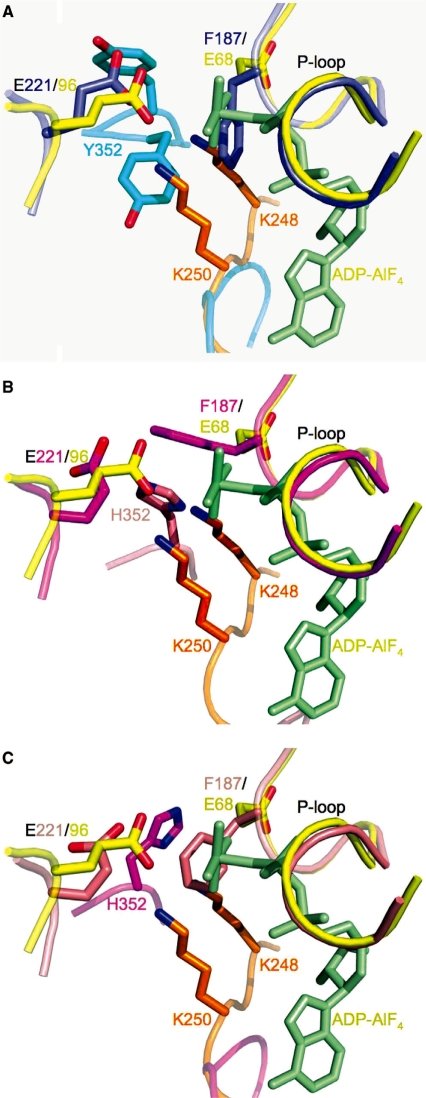
Figure 10.
Superposition of the Walker A and B motifs of E. coli RecA–ssDNA–ADP–AlF4 onto the Rad51–H352Y and -I345T mutants suggests a key role for P-loop residue Phe187 (Glu68 in E. coli) in sensing the gamma-phosphate or preventing the binding of ATP, and for residue 352 in assisting in catalysis. RecA is shown in yellow with its adjacent protomer in orange and its bound ADP-AlF4 in light green in these figures. (A) Superimposed Rad51-H352Y (purple) and its adacent protomer (cyan); (B) Superimposed ‘A’ protomer of Rad51–I345T (magenta) with its adjacent ‘D’ protomer (salmon); (C) Superimposed ‘D’ protomer of Rad51–I345T (salmon) with its adjacent protomer (magenta.) In (A) and (C), Phe187 of the P-loop is only 1.65 Å and 1.70 Å, respectively, from the AlF4 mimic of the γ-phosphate of the ATP. In (B), the δ-nitrogen of His352 is seen to be located almost exactly in between the amine groups of lysines 248 and 250 of E. coli, residues which have been shown to be essential for nucleotide hydrolysis.