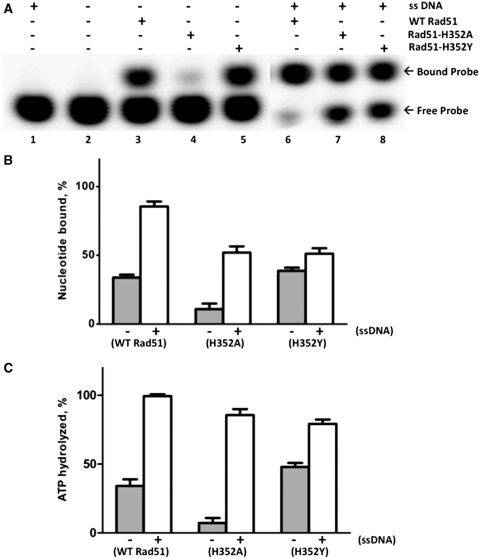
Figure 5.
Binding and hydrolysis of stoichiometric ATP by Rad51 and mutants. ATP binding and hydrolysis was measured at a 1:1 concentration ratio of protein to ATP. Nucleotide binding was measured by polyacrylamide gel EMSA, and hydrolysis was measured by TLC, as described under ‘Materials and Methods’ section. (A) 10 µM wild-type or mutant Rad51, as indicated, was incubated with 10 µM α-[32P]-ATP (10 µCi/ml) for 2 h either in the absence (lanes 3–5) or presence (lanes 6–8) of 30 µM φX174 ssDNA. Control experiments lacking enzyme or lacking both enzyme and ssDNA are shown in lanes 1 and 2, respectively. Samples were electrophoresed on native 12% polyacrylamide gels to separate free from bound nucleotide, which were detected and quantified by phosphorimaging. Other buffer components and assay conditions are described under ‘Materials and Methods’ section. (B) The percentage of bound nucleotide in (A), was quantified for each form of Rad51 in the absence (gray bars) and presence (white bars) of ssDNA. (C) The percentage of ATP hydrolyzed in samples identical to those analyzed in (A), was measured for each form of Rad51 protein in the absence (gray bars) and presence (white bars) of ssDNA.