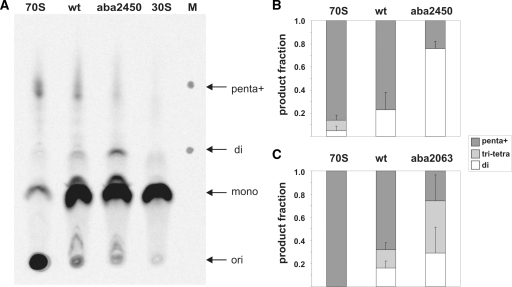
Figure 4.
Effects of A2450–C2063 base pair disruption on the length of the produced poly(Phe) peptides. (A) A representative TLC plate with poly([14C]Phe) peptides synthesized in poly(U)-dependent translation reactions is shown. Lanes show synthesized poly([14C]Phe) peptides and unincorporated [14C]Phe after translation using ribosomes reconstituted with the wt oligo (wt), ribosomes reconstituted with the oligo carrying an abasic site at 2450 (aba2450), native E. coli 70S (70S) as a positive control and E. coli 30S subunits as a negative control. Arrows indicate the loading spots (ori), positions of unincorporated [14C]Phe (mono) as well as the location of di-Phe (di) and penta-Phe peptides (penta) identified on the marker lane (M). Note that peptide products longer than penta-Phe cannot be resolved by this system (indicated by penta+). For quantification the TLC plate was exposed to a phosphoimager screen and analyzed with the Image Quant software. The results of peptide length quantifications using aba2450 (B) or aba2063 (C) ribosomes are shown and compared to native 70S ribosomes as well as to reconstituted wt ribosomes. The produced poly([14C]Phe) peptides were grouped into the length categories ‘di’ (white), ‘tri+tetra’ (light grey) and ‘penta+’ (dark grey) peptides. Radioactivity values measured in reactions containing no 50S ribosomal subunits [30S in (A)] were subtracted as background values from the corresponding category areas. The total amount of poly([14C]Phe) detected on each lane was assigned as 1.0. Graphs represent the results of at least two independent in vitro translation experiments, whereas the error bars indicate standard error.