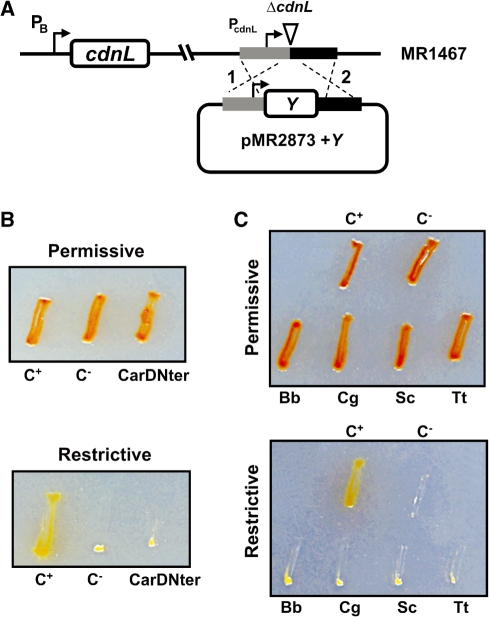
Figure 8.
M. xanthus CdnL cannot be replaced by CarDNter or by CdnL homologs from other bacteria. (A) Scheme showing the strategy used for complementation analysis. A plasmid derived from pMR2873, with ‘Y’ (CarDNter, CdnL, or a given CdnL homolog) under PcdnL control and DNA segments flanking cdnL upstream (grey) and downstream (black) in the genome, was introduced into the MR1467 strain conditionally expressing cdnL. Merodiploids resulting from plasmid integration by recombination at either ‘1’ or ‘2’ would exhibit constitutive expression of the inserted variant and conditional expression of the cdnL allele at the heterologous site. (B) Complementation analysis with CarDNter. The test strain ‘CarDNter’ resulted from using pMR2873 with ‘Y’ = CarDNter coding sequence; C+, is the positive control derived from using pMR2873 with ‘Y’ = cdnL, and the negative control C− is the recipient strain MR1467. (C) Complementation analysis with BbCdnL, CgCdnl, ScCdnL, and TtCdnL. Test strains were generated using the pMR2873 with ‘Y’ = cdnLBb (‘Bb’), cdnLCg (‘Cg’), cdnLSc (‘Sc’) or cdnLTt (‘Tt’). C+ and C− are as in B. In B and C, cells grown on CTT plates in the light were streaked on CTT plates ± B12, then incubated at 33°C for 2 days under permissive (plates without B12 incubated in the light) or restrictive conditions (plates with B12 incubated in the dark). The red colour in the light is due to carotenogenesis.