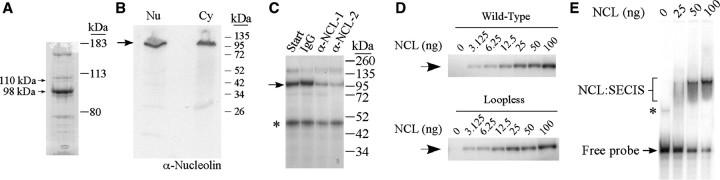
Figure 4.
Purification and identification of the crosslinking activity. (A) The fraction eluted from the PHGPx RNA affinity column was analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. The 110 and 98 kDa proteins indicated by the arrows were submitted for peptide sequence analysis by mass spectrometry and both bands were identified as nucleolin. (B) Nuclear and cytosolic extracts (30 µg) were analyzed by western blotting using an anti-nucleolin antibody. The arrow indicates the position of nucleolin. (C) Nuclear extracts from McArdle 7777 cells (30 µg) were immunodepleted with purified IgG or affinity purified anti-nucleolin antibodies (α-NCL-1, from Sigma; or α-NCL-2, from Novus Biologicals). Aliquots of starting material (Start) and the depleted extracts were analyzed by UV crosslinking with the 32P-labeled wild-type PHGPx SECIS probe as described in the legend to Figure 1. The 110 kDa crosslinked product is indicated by the arrow. The asterisk indicates an unidentified protein of ∼50 kDa. (D) The 32P-labeled wild-type PHGPx SECIS (top) or loopless RNA (bottom) probes were incubated in the presence of varying amounts of nucleolin purified from HeLa cells as indicated. The samples were analyzed by UV crosslinking. The arrow indicates the position of the crosslinked product. (E) REMSA assay using the 32P-labeled wild-type PHGPx SECIS probe, which was incubated with increasing amounts of nucleolin purified from HeLa cells, as indicated. The reactions were analyzed by non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. The nucleolin:SECIS complexes (NCL:SECIS) are indicated by a bracket. The asterisk may represent a slowly migrating conformation of probe.